Best Practices for Avoiding HIPAA Violations in Healthcare
We recently covered a list of some standard security features built-in to most electronic health record (EHR) systems. These features help users avoid damaging HIPAA violations and data breaches that could drive patients to other practices, and include the following:
ONC-ATCB Certification
Audit trails
Password protection
Data encryption
If you already have an EHR system in place, you probably already know what kinds of features these software systems offer.
What you might not know is that simply buying and using a HIPAA certified EHR system does not mean you’re in the clear when it comes to potential HIPAA violations in healthcare.
The majority of the healthcare HIPAA violations (41 percent) reported to one insurer in 2017 were caused by human error—i.e., unintended disclosure—rather than software malfunctions or hackers.
Causes of Data Breach in Healthcare Sector Among Beazley Clients
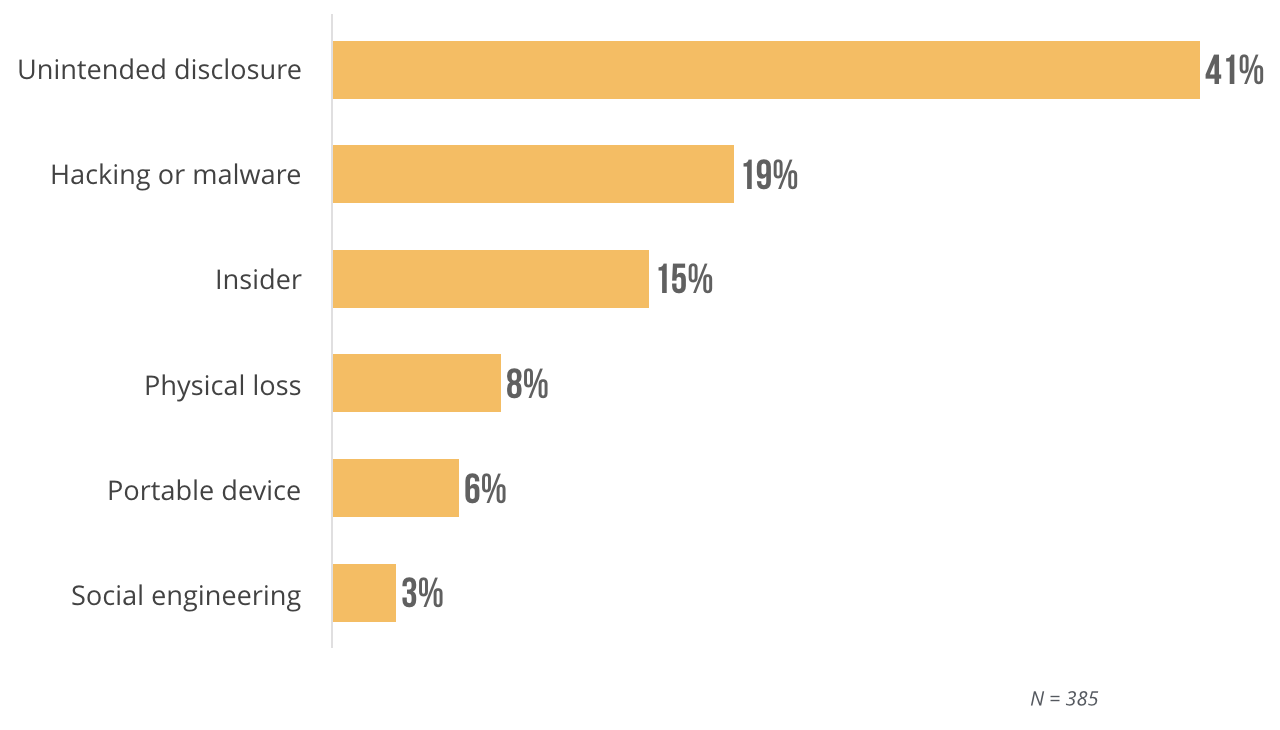
These numbers come from insurance claims with data breach insurance provider Beazley Group. This tells us that far too many practices are failing to properly train staff on how to use EHRs in a way that ensures patient privacy.
A HIPPA certified EHR does not guarantee compliance. Physicians must enact HIPAA security standards for using EHR systems and effectively train their staff if they hope to minimize the threat of a security breach.
Following the best practices laid out in this article will enable your practice to prevent all kinds of HIPAA violations, including the most common:
Impermissible use or disclosure
Lack of safeguards to protect written and electronic patient information
Lack of patient access to their own information
Use or disclosure of more than the minimum necessary patient information
According to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Service
In this article, we’ll cover five user best practices to protect patient privacy, prevent data breaches and ensure complete HIPAA compliance.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
Keep Your Devices Secure and Updated
Protect Your Systems with Anti-Virus Software and Proper Configuration
Train Your Team on HIPAA Security Practices
The Benefits of These Best Practices
Keep Your Devices Secure and Updated
QUICK TAKEAWAY: A lot of accidental disclosures happen because of the way devices are handled—or, rather, mishandled. The good news is you can prevent a lot of that by updating your software and securing your devices.
Keep Everything Up-to-Date
Whether you’re working with licensed, on-premise software or cloud-based software, it’s crucial that you stay on top of any software updates to your system. While many systems are capable of performing automated updates, it’s still wise to double check at least weekly to make sure you don’t miss any major security updates.
The same goes for your operating system, too.
And set aside some time periodically to go through your user accounts and old files to make sure you’re clearing out anything that’s no longer needed or in use.
Secure Your Mobile Devices
Thanks to the wonder of modern technology, EHR software can be deployed almost anywhere—on laptops, tablets and even cell phones. That’s great for users who want access to their system on-the-go, but this flexibility brings risk.
Users must take precautions to secure every device with access to patient information.
First of all, you’ll want to encrypt any data that might be shared remotely to ensure only authorized users are able to view it. From there, it comes down to user habits. Make sure anyone with remote access to patient data follows these guidelines:
If a mobile device is lost or stolen, report it immediately.
Do not access private patient data in public areas where other people can easily view it on your screen.
Do not connect to public Wi-Fi networks when working with private patient data.
You should also enact a clear and strong office policy regarding who can access data remotely and how those users should behave when working with secure data outside your practice.
Protect Your Systems with Anti-Virus Software and Proper Configuration
QUICK TAKEAWAY: Because EHR software can be accessed in a variety of ways, it’s important to equip your system with anti-virus software and then check for software vulnerabilities to avoid HIPAA violations.
Install Reliable Anti-Virus Software
If you go back and look at the leading causes of data breaches in 2017, you’ll see that systems being hacked was the second largest reason for HIPAA infractions, and the most common way hackers get into EHR systems is through viruses or other malware.
Computers can be infected with these viruses in a number of ways, such as with:
CDs
Flash drives
Emails
Web downloads
It’s crucial to install a trustworthy, reliable anti-virus software and keep it up to date to avoid viruses, which can compromise or corrupt patient data.
You’ll buy anti-virus software independently from your EHR system, so make sure you dedicate resources for additional research to find the best product to protect your practice and patients.
While we’re on the subject of protection, consider installing a firewall to keep hackers or other unauthorized intruders from accessing your network. Firewalls work well with anti-virus software to create a two-pronged defense that will make your EHR system that much more secure.
Check for Vulnerabilities
Once you settle on your EHR system, you’re going to need to make strategic decisions about how the software will be set up on your computer.
This is called configuration management, and it involves disabling any applications that you won’t be using (for example, if your practice has no need for instant messaging with patients, yet the EHR system came with that feature built-in).
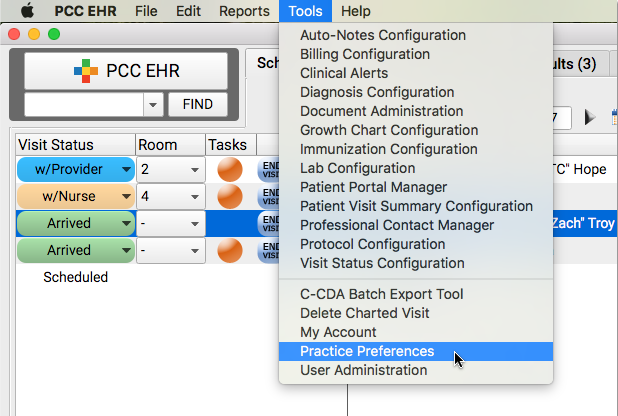
PCC EHR enables users to control application preferences
By minimizing the number of applications and eliminating those you won’t use, you reduce the overall number of potential vulnerabilities within your system.
Take instant messaging as an example: If you don’t use it to communicate with your patients, yet leave it enabled within your system, an untrained employee could mistake it for a usable tool and accidentally disclose patient information.
You’ll also want to double check whether or not the EHR vendor maintains access to their software once it’s installed—through what’s called a back door—for purposes of automating updates or offering technical support.
If this is the case, you’ll want to make sure that connection is secure or disabled. Taking these steps will keep anything from happening within your EHR system without your knowledge in order to prevent accidental disclosure.
Restrict Access to Data
QUICK TAKEAWAY: A big part of preventing unintended data disclosure and other human errors that lead to data breaches is being strategic and thoughtful about who you allow to access your secure information and how their passwords are being stored.
Implement User-Based Access Controls
Many EHR systems enable users with management access to create access control lists. Basically, you can designate clearance levels and assign them to specific usernames. Doing this gives the people in your office permission to view the data they need in order to complete their responsibilities, and nothing more.
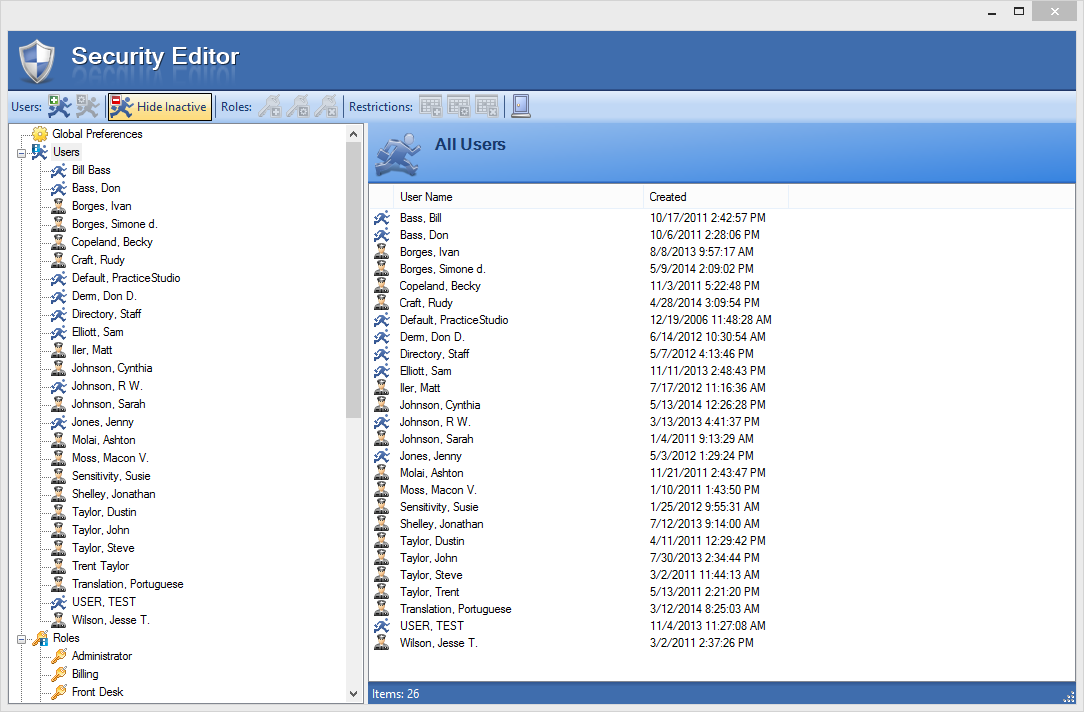

User permission controls within Practice Studio
Enact Strict Password Protocols
This is another two-part approach to securing your system because you’re going to want to:
Make sure the passwords being created are complex and difficult to guess.
Make sure users are taking precautions when storing passwords.
The first task is fairly easy to address. Set requirements: minimum character length, a certain amount of numbers, a specific combination of upper and lower case letters and use of special characters. Reject passwords that don’t meet these requirements.
The second task is slightly more difficult because it requires users to form their own acceptable habits to remember their unique passwords, which isn’t always easy.
One way to work around that is mandating a password change regularly (most practices go with once every other quarter). Anything you can do to make accessing your system harder for hackers is good, and regularly changing passwords is a step towards that goal.
Train Your Team on HIPAA Security Practices
QUICK TAKEAWAY: There’s one thing that can completely negate all of the time and money you put into security: users. The biggest threat to your patients’ privacy are your own employees, and for that reason you must impress upon your team the importance of following these security best practices.
Create a Security Training Program for New Hires
Regardless of new hires’ experience or skill level, your training program should bring every new employee up to the same speed regarding the practices and protocols that are unique to your team.
This training should include reviewing documentation of the best practices covered above, as well as additional reference guides that you create for specific practices.
For example: a step-by-step process doc explaining how your team goes about sending appointment reminder emails, where new (and existing) team members can double check to make sure they’re following all the rules correctly.
Encourage Hypervigilance Among Your Team
When it comes to protecting your patients and your practice, you can’t afford to get complacent. To prevent human error from creeping into the equation, you should find way to instill a sense of gravity within your team when it comes to all things HIPAA-related.
A few ideas to accomplish this include:
Creating and using checklists for all security-based tasks (such as changing passwords, working remotely etc.).
Posting guidelines in staff areas so your team can review them at any time.
Sending out newsletters with HIPPA violations in the news, up-to-date statistics about data breaches or any other security-related facts or stories that might encourage readers to take precautions.
Offering ongoing security trainings to keep your best practices top-of-mind for everyone on the team.
Designate one team member as the patient privacy manager to be the go-to for all things EHR security and HIPAA related.
The key is to find methods that work for and motivate your unique team. After all, you’re all in the business of protecting your patients and your practice’s reputation together.
The Benefits of These Best Practices
The penalties for HIPAA violations can include fines ranging from $100 to $1.5 million and possible jail time for certain charges categorized as willful neglect.
HIPAA violations that affect at least 500 patients are shared publicly by the Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights, published on what has become known as the “Wall of Shame.”
All that to say the benefits of implementing strict best practices for handling patient information and using EHRs include avoiding:
Costly fines and settlements
Public shaming
Loss of patients
So regardless of whether your practice has dealt with a HIPAA security breach or not, it’s in your—and your patients’—best interest to go ahead and adopt these best practices in order to avoid potential violations.