How Small Practices Can Overcome IoT Security Challenges
From smart devices that monitor patients’ vitals to mobile apps that remind people to take their prescribed medicine, the internet of things (IoT) is becoming an essential part of health care.
But, the security of IoT devices is a big challenge for medical practices, regardless of their size. IoT security risks in health care are much higher than other industries because IoT-connected devices contain confidential data, e.g., patients’ social security numbers and personal health records, which are often targeted by cybercriminals.
In 2017, the misuse of connected medical devices by staff members resulted in 41 percent of IoT-related security issues in the U.S. health care industry. This is a huge issue that should be tackled immediately to protect patients and their data.
Small medical practices that don’t implement adequate security measures can face dire consequences such as data theft, loss of credibility, regulatory fines and potential closure.
In this article, we’ll help you identify the risks and guide you on ways to implement better IoT security.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
Majority of Patients Worry About Data Security
Small Practices Face Many IoT Security Risks
Measures to Overcome IoT Security Risks
Majority of Patients Worry About Data Security
The majority of U.S. consumers are strongly concerned about the safety of their personal health data. However, they do support the use of IoT tools for added convenience, as long as they feel they have control over when and how they’re monitored.
The 2017 Unisys Security Index, an online survey of 1,000 adults, revealed that 78 percent of Americans are concerned about unauthorized access to their internet-connected medical devices, such as defibrillators, pacemakers and insulin pumps.
Patients want their doctors to be immediately notified through these internet-connected devices about any significant changes in their health data.
Americans’ Concerns Over Personal Health Data
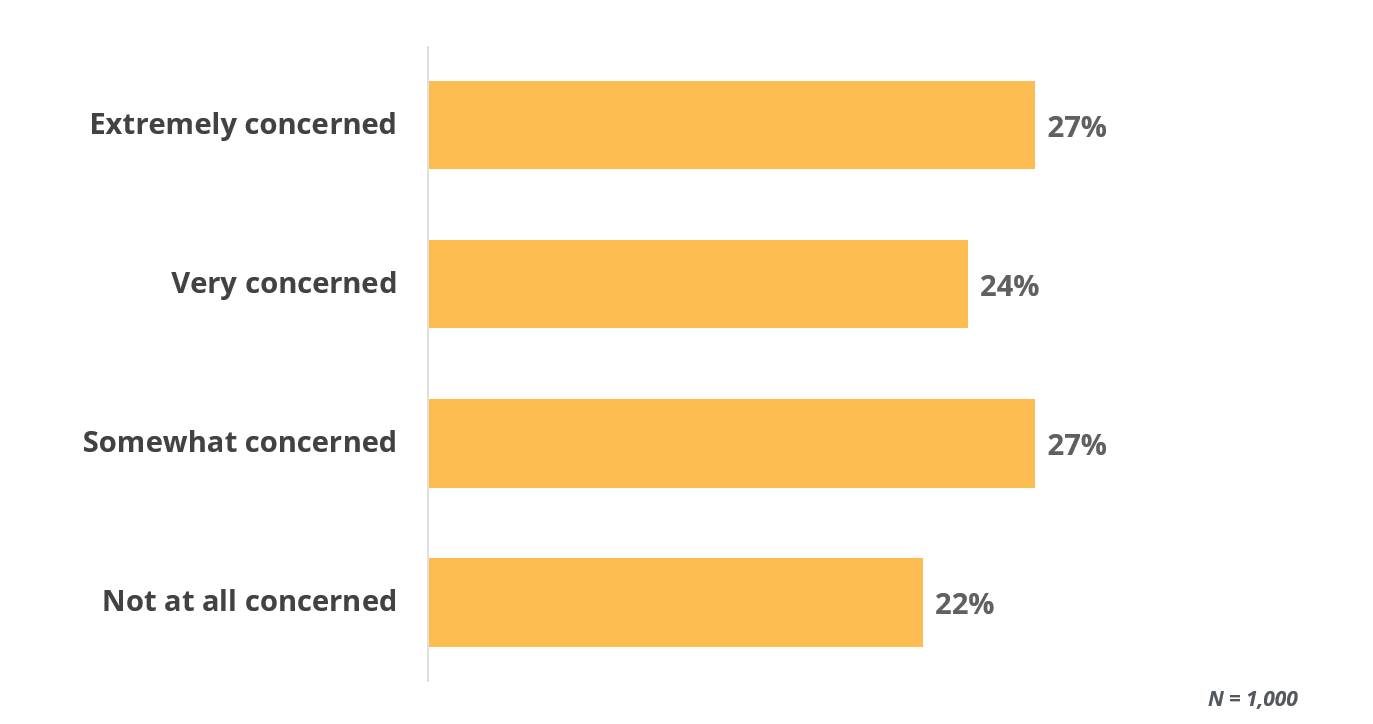
The survey found that 51 percent of Americans are either extremely concerned or very concerned that someone could gain unauthorized access to their IoT-enabled medical devices.
Therefore, medical practices should take concrete and immediate steps to address these concerns and ensure that the personal health data generated and stored in patients’ IoT-connected medical devices is completely safe.
Our next section discusses in detail how you can address security risks, and by extension, patient concerns.
Small Practices Face Many IoT Security Risks
As we stated above, the stakes of IoT-related security threats are much higher in the medical industry. Electronic health records (EHR) systems contain a lot of patients’ personal data, including social security numbers, medical history and appointment dates, which can cause a lot of harm in the wrong hands.
When unsecured EHR systems come in contact with other medical devices connected to the internet, cybercriminals are able to easily steal patient data. This means that a lack of proper IT security standards in your small medical practice could result in the online theft of patient records.
This risk isn’t new: Internet-connected medical devices have been vulnerable to threats for a long time.
Back in 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned about security flaws in smart infusion pump devices and alerted the medical community that hackers could intrude into these devices and risk patients’ lives. And in 2016, St. Jude Medical warned about a similar attack on smart cardiac devices.
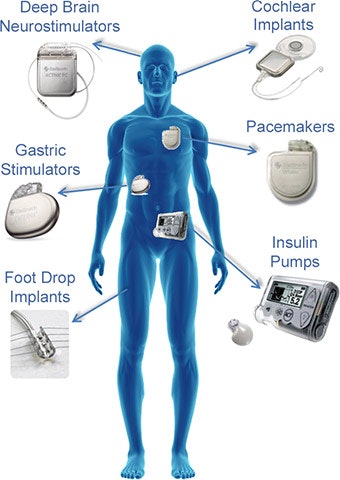
Common internet-connected medical devices vulnerable to hacks (Source)
All the medical devices you see above are highly prone to cyberattacks. In 2017, the FDA recalled nearly half a million pacemakers, which were already installed in patients, due to cybersecurity issues. It feared that hackers could alter the heartbeats of patients or discharge their batteries.
Security risks can also arise from health care-related mobile applications. Small medical practices should be very careful about the devices they use and how they use them.
Two of the most common and most high-risk scenarios include:
A BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policy, which is considered one of the biggest contributors to data security risks in medical practices. It’s tough to scrutinize and control all the personal mobile devices (smartphones, tablets and laptops) that connect to your IT network every day.
A staff member introducing a stand-alone device, such as an infusion pump, into the practice’s network without informing the IT team. This could cause multiple network and connectivity glitches that would result in data loss or unauthorized data migration.
Measures to Overcome IoT Security Risks
As we saw above, IoT security risks are quite high and you should identify potential risks in your practice so that you can deploy methods to address them.
Here are our recommendations for how small medical practices can address potential IoT security risks:
Ensure Proper Authentication
Small medical practices that use connected devices must ensure that proper authentication is in place to access patient records. In addition to the usual login ID and password for the EHR systems, practices must install two-factor authentication system for sign-ins, as it can reduce your chances of being hacked.
A two-factor authentication system requires users to provide at least one more form of personal identification, beyond login ID and password, to get access to electronically protected data such as voice recognition, fingerprint or a PIN.
This means you should choose and install an EHR system that offers a two-factor authentication security sign-in process.
For instance, AdvancedMD EHR’s e-prescribing technology, AdvancedEPCS, offers strict and multiple levels of security with two-factor authentication. Similarly, drchrono offers two-factor authentication in its EHR solutions for added security.
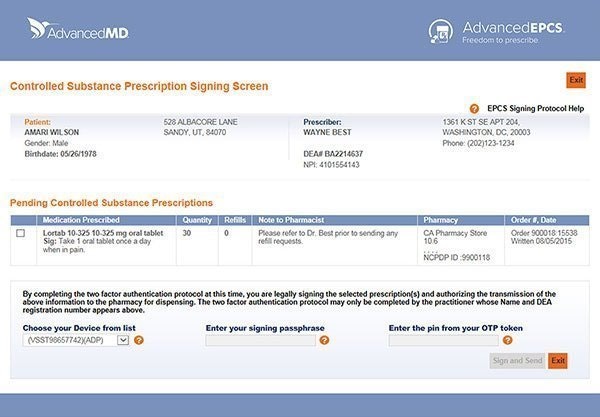

Two-factor authentication in AdvancedMD EHR’s AdvancedEPCS
Encrypt Your Data
Accessing EHRs via mobile device has become common and extremely convenient, though it poses great risks. Medical practices must encrypt patient data, when it’s stored and when it’s in transit, to minimize data breaches. If non-encrypted data moves from EHRs to other connected devices, it becomes easy for hackers to steal this data.
For data storage-related encryption, medical practices should ask their EHR software vendor to install hardware-level encryption. For data transit-related encryption, practices must ensure maximum usage of its internal Wi-Fi network and prohibit data transfer over cellular networks, unless it’s extremely important.
Some vendors that offer this feature include athenahealth EHR, which uses HTTP over SSL (HTTPS) protocol for all communication related to protected health information (PHI) between the application and users. Another solution, CareCloud, uses 128-bit SSL Certification to protect customer data during data transfer to the customer’s network.
Install Secure Boot Configuration
When you install a secure boot configuration, it adds an extra level of security to protect patient data. When a computer is turned on, the secure boot guarantees that none of the existing configurations are tampered with.
Secure boot configuration is the process of booting up from the operating system with added security measures. It’s only possible if your computer’s hardware comes with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) firmware that communicates between the operating system and hardware. Secure boot configuration helps a computer resist infection and attacks from malware.
Increase Awareness Through Education and Training
With the continuous growth of new medical technologies, ensure that your medical staff is aware of the security challenges and risks and ways to address them. Provide clear and detailed instructions to your staff on ways to avoid security risks in the future.
Be sure to cover the following items when training your employees:
Encrypt and secure all wireless networks, servers, emails and mobile devices
Implement physical security controls
Install and maintain effective anti-virus software
Use strong passwords and update them regularly
The idea is to implement security measures that work for your employees. Being aware of and managing the security risks should be part of their daily activities and not an infrequent task.
What Can I Do Next?
IoT offers significant advantages to the medical and health care industry. As a small medical practice, relish the many benefits it offers but also bear in mind the security challenges and risks.
For your next steps after reading this article:
Regularly review and update your practice’s security policies, incorporating new measures, as discussed above, to avoid risks.
Set up a training for your staff members to increase awareness about the security risks in your practice.
Check with your EHR vendor to see what security features it offers. If it doesn’t offer sufficient security features, then start shopping for a new EHR. For a free consultation with a software advisor on the latest EHR software, call us at (844) 686-5616.