Which ERP Implementation Methodology Is Right for Your Business?
Did you know that 50% of ERP implementations fail the first time around? Failed implementation can result in wasted software spend and has the potential to hurt business profitability.
With stakes this high, it’s vital to choose an implementation approach that suits your existing IT setup. Selecting the right ERP implementation methodology will significantly reduce implementation errors, help avoid unrealistic expectations, and ensure that you stay within budget.
In this article, we’ve analyzed the three main ERP implementation approaches and suggested a tool that can help you decide which approach is the best for your business.
Key approaches to ERP implementation
There are three key approaches that you can use to implement an ERP system: big bang, phased, and parallel. Each approach has its inherent advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, you’ll need to thoroughly understand each type to select the one that best caters to your IT setup.
The big bang approach
In the big bang approach, ERP software is deployed for the entire organization in one go. This means that on the go-live date, the system will be deployed across business functions—manufacturing, operations, sales, finance, marketing, etc.
The big bang approach requires a lot of planning since the software is implemented, in most cases, on a pre-decided date. Also, the pressure to get things done right is high, as any error can potentially affect all business functions.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
It needs less time to deploy, as all changes are made in one go. | Deployment risk is high, as changes are implemented across business functions |
The overall cost of deployment is low. | More time is needed for planning the implementation. |
Only one-time training is required. | Changes are irreversible, so there’s high pressure on the implementation team to get things right the first time. |
The phased approach
In this approach, implementation is planned sequentially, with each phase implementing the ERP system for one or more business processes. You can plan these phases by business department, location, manufacturing facility, and more.
The phased approach takes more time to implement than the big bang method, but it provides a higher degree of safety because errors, if any, won’t be impacting all business operations. It also puts less pressure on the implementation team, as there are fewer things to worry about during each phase.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Lower implementation risk. | A longer implementation period. |
Errors can be fixed faster. | Data sync errors between the new ERP solution and legacy systems. |
Experience in one phase can help with implementation in subsequent phases. | It can be taxing for end users, as changes are made more frequently. |
The parallel approach
In the parallel approach, a new ERP system is implemented while running legacy systems in parallel. This minimizes implementation risks, as you can default to the legacy systems in case critical errors come up in the new system.
However, running two systems simultaneously invites technical complexities, such as data synchronization issues. It also adds to the cost of implementation, since you’ll be relying on implementation as well as IT experts throughout the process.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Implementation risk is minimal, so it’s suited for critical processes. | It’s expensive to implement. |
Implementation is slower than the big bang but faster than the phased approach. | Data entry issues are likely, as data needs to be recorded both in the old and new systems. |
End users can learn features in the new system while still using the old system for daily tasks. | There are technical complexities involved in running both systems in parallel. |
The implementation methodology selection tool
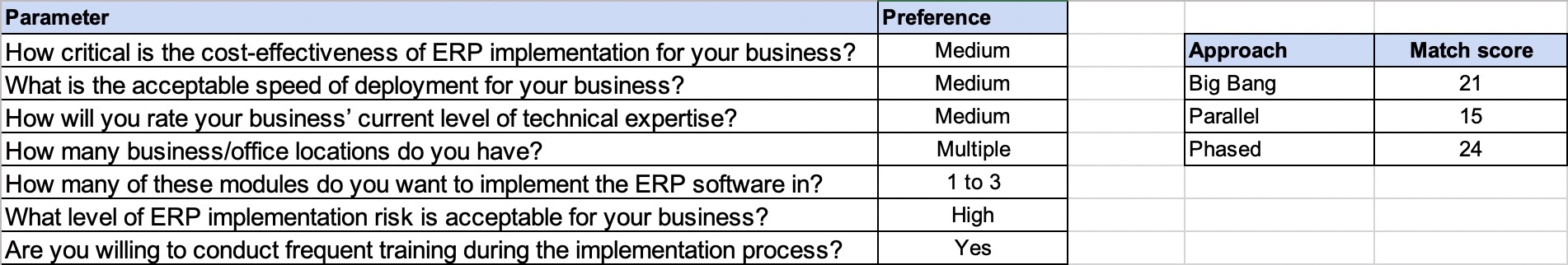
The ERP implementation methodology selection tool helps identify the right implementation methodology for your business by factoring in your requirements and key preferences. It asks the following questions and suggests options based on your response:
How critical is the cost-effectiveness of ERP implementation for your business?
Pricing is one of the biggest considerations when implementing an ERP system. If you’re on a strict budget, select High from the drop-down list. If your budget is flexible, select Low or Medium.
What is the acceptable speed of deployment for your business?
For this question, there are three options to select from: Slow, Fast, and Medium. We recommend opting for Medium or Slow, unless absolutely necessary, since faster deployment entails higher implementation failure risks.
How will you rate your business’ current level of technical expertise?
To answer this question, you’ll need to assess the following tech-related areas:
Is your tech staff proficient in database migration and management?
Does your business have dedicated IT professionals for software deployment?
Is your tech staff capable of troubleshooting deployment issues?
If the answer to all of these questions is a yes, select High from the drop-down list. If the answer to any two is a yes, then select Medium. However, if the answer is yes for just one, select Low.
How many business/office locations do you have?
Select an option based on the number of business locations you want to deploy the ERP system in. Exclude warehouse locations in the count.
How many of these modules do you want to implement for your ERP software?
Select the number of core ERP modules you want to include in the ERP system. The tool considers the following seven ERP modules as core:
Finance
Manufacturing resource planning (MRP)
Supply chain management (SCM)
Inventory management
Customer relationship management (CRM)
Human resources (HR)
Accounting
Analytics
What level of ERP implementation risk is acceptable for your business?
This selection requires you to assess your current risk appetite for ERP implementation. If implementation failure could jeopardize your entire business operations, select Low from the drop-down list. If your business processes have high interdependencies, we recommend not selecting High.
Are you willing to conduct frequent training during the implementation process?
Each implementation type has different training needs; therefore, you must decide beforehand if you’ll be able to take the training load. Select Yes or No based on the availability of time and resources.
Download the ERP Implementation Methodology Selection Tool
How to use the match score?
After you’ve entered your preferences in the tool, you’ll get a “match score” for each of the implementation types. The score is indicative of how well each approach aligns with your business requirements. Based on your score, you can ascertain the right ERP implementation methodology for your business.
In some cases, the scores can be close, making it difficult to reach a final decision. In such cases, review your preferences and make them more restrictive.
Looking for more? This video introduces great ideas for successful ERP implementation.
Next steps
Once you’ve decided on an implementation approach, the next step is selecting an ERP tool. To find software that’s right for your business, we recommend using the following resources:
ERP software buyers guide: This guide covers all the essential information you’ll need to make a purchase decision.
ERP software catalog: This resource lists the different types of ERP solutions available on the market. You can filter products by business size, industry, pricing, and rating. You can also read product descriptions and user reviews.
ERP FrontRunners report: This report positions the top ERP solutions based on user ratings and usability.
For more personalized assistance, schedule an appointment with our ERP advisors for a free, no-obligation consultation. Our advisors provide software recommendations that meet your needs.