The Benefits of Adopting RPA For Your Accounting Functions
In today’s world of high-speed information and pressing deadlines, efficiency is one of the most sought after qualities in all business processes. Yet within accounting, many SMB leaders and account managers still struggle to increase their efficiency in daily accounting tasks. This is where robotic process automation (RPA) comes into play.
If you are an SMB leader overlooking the finance department or an accounting manager that is looking for ways to keep your processes flowing at peak performance, RPA is the key to bringing your accounting functions up-to-date and maximizing efficiency.
Let’s take a further look at what RPA is and how it could help you streamline your accounting processes.
What is robotic process automation?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a productivity tool that allows users to configure scripts or “bots” that imitate selected tasks within a process. These processes may include manipulating data, exchanging information from system to system, triggering responses, or even executing transactions. RPA helps businesses to automate and optimize these processes, reducing repetitive work and enhancing employee productivity.
For instance, your team may still be spending hours in front of spreadsheets manually entering/retrieving data or transferring numbers—these are the perfect tasks for RPA bots to step in, take over, and begin to automate.
If your company is already using accounting software, it doesn’t mean RPA isn’t for you. Rather, RPA can be used alongside these other applications to bridge the gap between disconnected processes, or to integrate separate accounting and finance tools, with numerous benefits to managers and employees alike.
What are the benefits of RPA in accounting?
The RPA industry is growing rapidly, as businesses are becoming increasingly aware of the benefits of digitizing their processes—in 2021 alone, the RPA software market grew by 31% to $2.4 billion [1].
In addition, industries such as manufacturing have already seen the success of RPA implementation by streamlining the assembly of everything from automobiles to small cellular components.
As RPA makes its way into accounting, the following are a few areas that can derive real benefits from robotic automation.
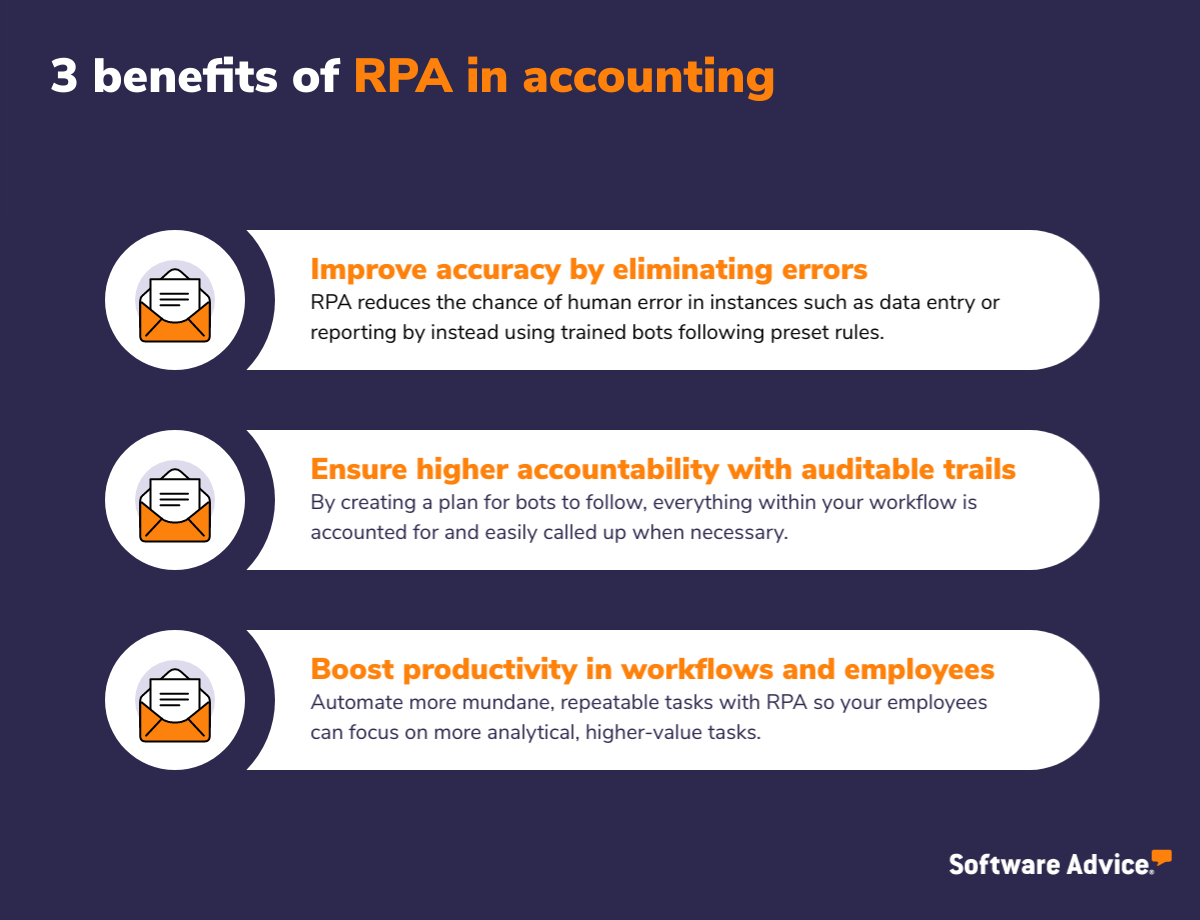
Improve accuracy with RPA by eliminating human errors
Despite everyone’s best efforts, to err is human—but in accounting, a simple numerical mistake can lead to drastic losses down the road and countless hours of corrections. RPA reduces the chance of human error in instances such as data entry or reporting by instead using trained bots following preset rules to handle data.
According to Gartner research, human error within the finance function produces, on average, 25,000 hours of avoidable rework at a cost of $878,000. [2] RPA bots provide consistent results based solely on the data provided, leaving you with continued higher accuracy and accountability.
Ensure higher accountability with easily auditable trails left by each RPA bot
Given the constantly changing regulatory environment, having a seal-proof paper trail to look back on is a necessity in accounting and finance processes. By creating a well-thought-out plan for the bots to follow, everything within your workflows is accounted for, from accesses made to every generated output.
All these data points are stored in a database, holding relevant parties accountable for all bots’ actions. All this reviewable information at your fingertips increases compliance while decreasing the chance for fraudulent activities to go unregistered.
Boost productivity with RPA not only in workflows, but also in employees
Since RPA bots mimic human actions in a given workflow, such as filling in forms, moving files, or scraping data, the employees that had previously been required to do these things are now free to focus their time on more analytical, higher-value tasks.
These practices are also scalable to match your company needs, as RPA bots are able to tackle massive amounts of data. Let’s say there’s an influx of invoices or payment orders to process, or large legacy systems that need to be overhauled and have data exchanged. Rather than deploying numerous employees, a set of processes can be established and the bots can get to work. RPA provides accounting teams room for growth while keeping productivity at its peak.
Examples of RPA in accounting
From capturing financial data to auditing it, and every step in between, the effectiveness in which RPA can handle systematic tasks comes to light within these accounting use cases.
Streamline invoice processing with bots
Teams who handle a large number of invoices on a regular basis know how tedious processing them can be. Invoices can vary in format, quality, and even language. RPA bots are able to extract the correct data using optical character recognition (OCR) and machine learning capabilities, and relay that information to the correct end destinations. RPA can automate this entire process, reducing manual invoice hand-offs, and leaving only the rare outlier for human inspection.
Automate recurring steps in recording and reporting
After taking the extrapolated data from invoices (or any financial numbers, such as expenses, revenues, debt, equity, etc.), the bots can be taught to record journal entries, mimicking the human process. All journal entries are logged with an accessible history of origin, keeping in line with compliance regulations in even the most basic accounting functions.
After the journal entries are made, RPA bots can close the ledgers and use this data to generate financial reports, sending the entries to the correct line in the financial statements and reducing discrepancies from manual data transfer.
When it comes to financial reporting, minimizing the possibility for mistakes while maintaining compliance on regulatory audits is a key priority. Adopting RPA can automate the complete process from initial recording to financial reporting, freeing employees to spend more time analyzing the bottom line and building deeper insights. All this is done while maintaining a complete audit trail.
Optimize internal auditing processes
Although auditing automation should be handled at a slower pace to assess effectiveness, the outcome can be extremely valuable. In general revenue audits, RPA can manage the comparative tasks of checking accuracy in cash flows, which is especially helpful when having to check between multiple systems. This removes a lot of the legwork for employees and drastically reduces the time spent staring at spreadsheets.
For reconciliations, RPA bots can take over the repetitive tasks related to each entry, whether it’s a periodic ledger reconciliation or advanced reconciliation on a chain of transactions, leading to more efficient audit outcomes. And just like with invoice processing, any exceptions can be flagged for a higher authority’s review, playing to the advantages of RPA’s rules-based manner.
Potential roadblocks to implementing RPA in automation
Although RPA yields many benefits for automating accounting functions, there are a few roadblocks to consider before deploying it in your own systems.
The first is the common hesitancy to remove human judgment from processes involving crucial financials. It’s important to remember that humans still have control over robotic accounting. RPA bots follow rule configurations set by the user, and the user is always there to review the set processes and any potential exceptions. The continuous monitoring and updating of RPA bots are a key role in successful adoption.
This leads into one of the biggest roadblocks to implementing RPA, which is creating and standardizing the configurations for bots to follow. You shouldn’t be too hasty with RPA implementation, because if the set processes the bots are following are not complete or up-to-date, it will lead to continuous automated errors. It’s important that the accounting processes are broken down into steps beforehand, following business rules. Those responsible for implementing RPA can identify improvements in the process by trimming repetitive tasks and selecting which steps can be optimized using RPA.
The persons responsible for implementing RPA tools will also need to be trained. Although RPA doesn’t require as much IT involvement as other prebuilt accounting software, those executing RPA will need to learn the basic functions of it and how to create simple RPA scripts for the bots to follow. They will also need a knowledgeable foundation of accounting skills and functions.
If you’d like to do some more specific reading about roadblocks to implementing RPA in financial reporting, you can find more information here: Obstacles to Using RPA in Financial Reporting.
Wondering what to do next?
RPA continues to grow as a common toolset for accounting teams across various industries and sectors. By adopting RPA in your own accounting functions, you can gain a competitive edge by transforming your accounting procedures. Increasing efficiency no longer needs to be a reoccurring business challenge on the meeting calendar.
In evaluating whether or not your accounting methods are a good fit for RPA, be sure to remind hesitant coworkers that RPA is there to make their lives easier, not to replace them. Despite the use of robots, it’s the people directing them that are crucial to their success. They are the ones who will be closest to the bot configurations and the ones to see the most immediate results.
If your accounting department is ready to overcome these roadblocks and reap the benefits of RPA, you can find and compare the best RPA products and tools in the Software Advice directory.