Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Shift From Manual to Cutting-Edge Medical Software Solutions
While planning to purchase medical software, 65 percent of healthcare businesses waited until after evaluating a few products to set their budgets, according to our 2023 SMB Medical Software Buying Trends Survey.*
Ultimately, it is crucial to identify the most suitable software tools, given their significant impact on healthcare operations. This is why Software Advice advisors speak with thousands of decision-makers to diligently assist them in evaluating and selecting software solutions that align with the specific needs of their healthcare organizations.
Recently, we mined those conversations for insights about budgets, feature needs, and pain points to aid your own software search.
Key insights
Many healthcare practices are transitioning from manual or non-automated methods to using medical software solutions.
The adoption of medical software is primarily motivated by the improved functionality, user-friendliness, and increased efficiency offered by these solutions.
The average budget range for buyers of medical software per provider, per month falls between $388 and $432.
Buyers and users both prioritize essential medical functionalities such as electronic medical records (EMR), patient scheduling, medical billing, ePrescribing, and telemedicine.
Most practices shift towards using medical software from no or manual methods
Our advisors asked buyers about their choice of current methods over the past three years. Our data from September 2021 to August 2023 unveils a significant increase in the percentage of buyers switching to medical software from manual methods or no method at all.
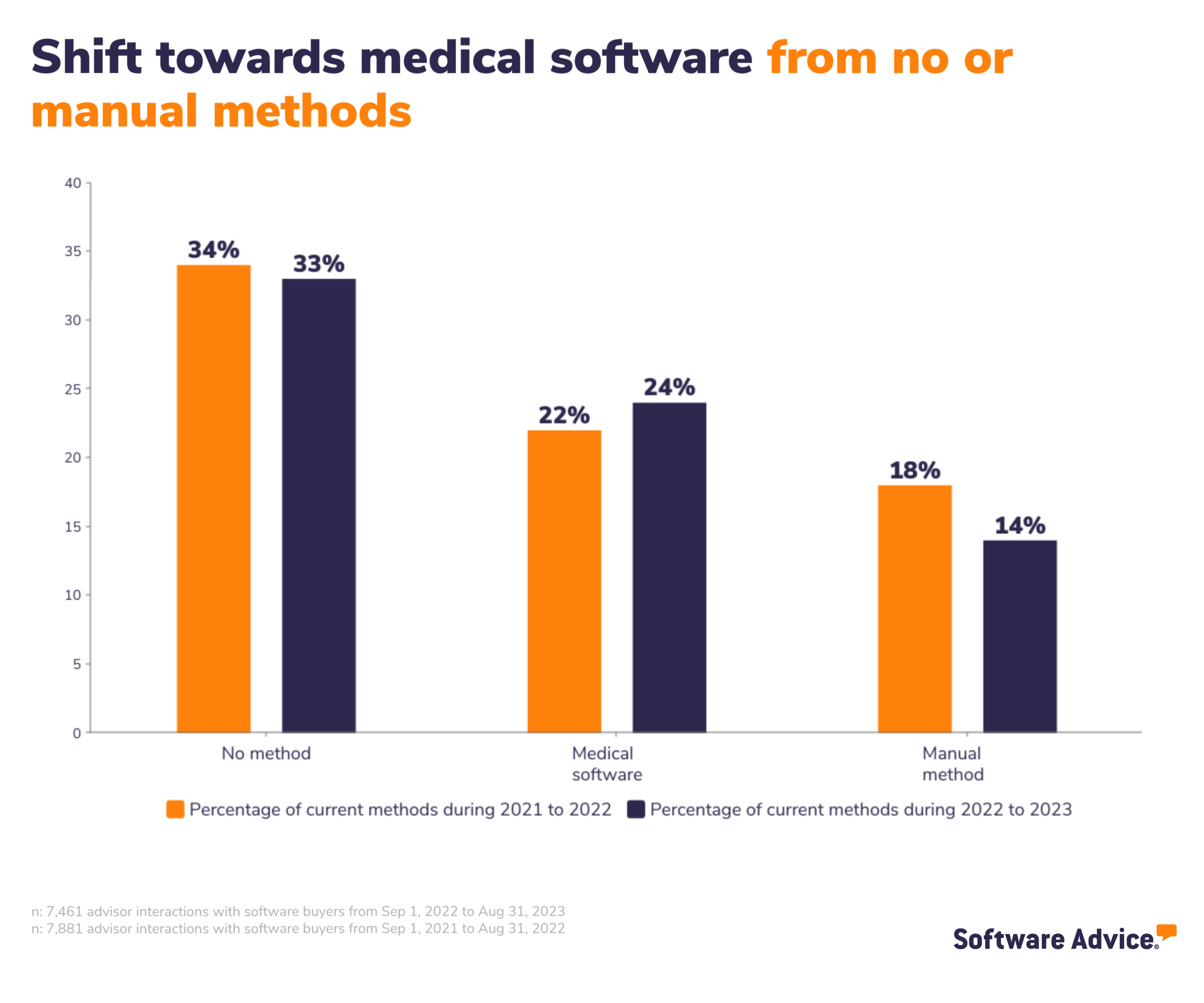
The rising percentage of buyers switching to medical software from manual or no methods can be attributed to its compelling benefits. For instance, electronic health records (EHR) software ensures regulatory compliance, reducing the risk of legal repercussions and fines. It also enhances patient care by providing instant access to comprehensive patient records, promoting collaboration among care teams, and offering tools for data analytics and reporting. Moreover, EHRs improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and facilitate telemedicine integration, making them an essential tool in modern healthcare. Additionally, patient engagement is enhanced through EHR patient portals, resulting in higher patient satisfaction and involvement.
Limited functionality, user-friendliness, and better efficiency drive users to switch to a new medical software
The conversations our advisors had with existing users of medical software who want to replace their system (i.e., 24%) provide real-life challenges that businesses face with their current tool. These buyers say there are three main reasons they are switching their medical software: limited functionality (27%), lack of user-friendliness (19%), and inefficiency (19%).
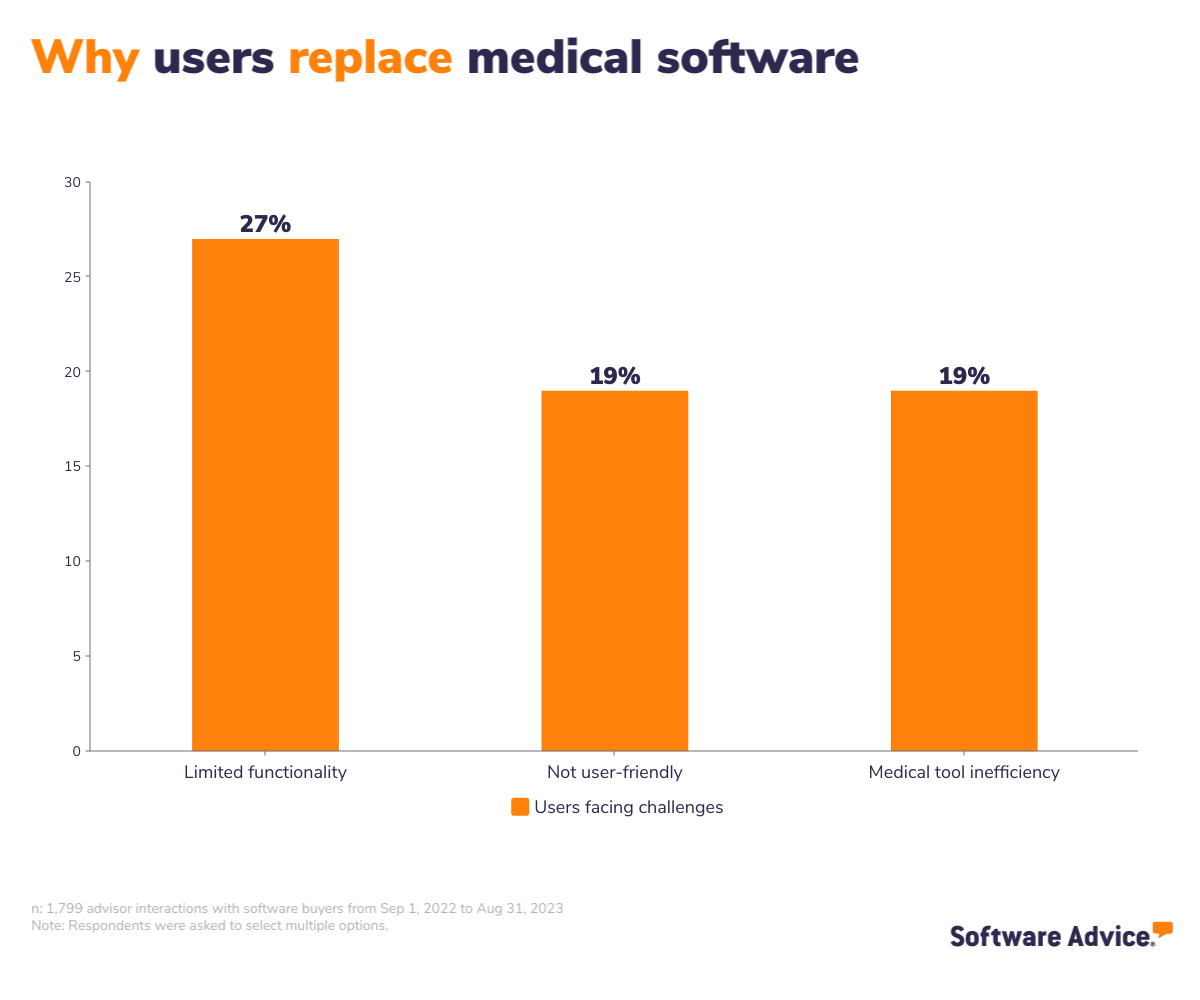
Inadequate functionality within medical software significantly hampers users' capacity to efficiently manage their daily medical operations. To illustrate, some medical software lacks seamless integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems. In this case, healthcare providers may find it challenging to access comprehensive patient medical histories, including crucial data on past diagnoses, treatments, and allergies. This limitation not only prolongs the time required for patient consultations but also increases the risk of medical errors due to incomplete information, potentially compromising patient safety and the overall quality of care provided.
Lack of user-friendliness in medical software can create significant challenges for users, particularly healthcare professionals. For example, a physician using a medical software system with a non-intuitive interface for prescribing medications might struggle to select the correct medications, dosages, and frequencies efficiently if the system's layout and navigation are unclear. Ultimately, this not only consumes valuable time but also increases the risk of medication errors, which can have severe consequences for patient safety. The frustration and difficulty in using the software can lead to reduced productivity and potential compromises in patient care.
Inefficiencies within medical software can be a source of frustration for users due to their adverse impact on productivity. For example, if a medical billing solution lacks automation features and requires manual data entry for each patient encounter, it can lead to billing errors, longer administrative hours, and a higher likelihood of revenue loss for a healthcare facility. This inefficiency not only impacts the staff's productivity but can also result in financial challenges for the healthcare organization.
Addressing these challenges can significantly improve the functionality of your medical software, making it more effective in managing crucial aspects such as patient records, appointment scheduling, and billing processes within a healthcare setting.
Average buyers' budgets range from $388 to $432 per provider, per month
In the medical industry, a business’s software requirements are not solely contingent on its size, but there's a common trend where smaller medical practices often have more straightforward needs, whereas larger healthcare organizations require more advanced and comprehensive solutions. Consequently, it's logical that the amount buyers tend to budget per provider tends to increase as the size of the medical team or organization grows.
The chart below highlights the average buyer budget per provider, per month for increasing team sizes.
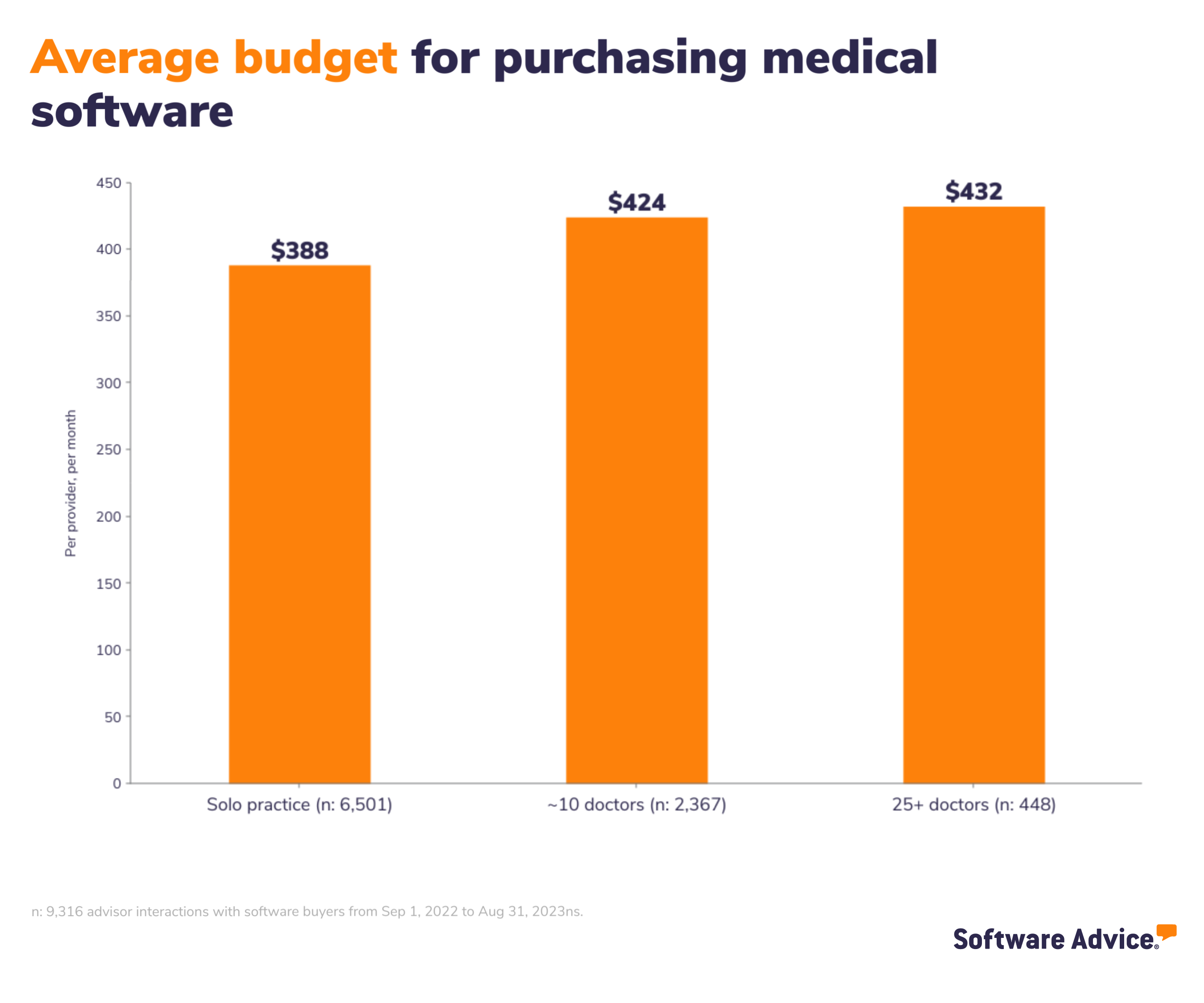
These budgets are roughly in line with the pricing our research team sees in the marketplace. The cost of medical software is heavily influenced by the required features such as EMR/EHR and/or practice management and the quantity of provider licenses needed. The most common pricing model is a monthly or annual subscription, often based on the number of providers.
Entry-level plans typically cover limited functionality such as electronic medical records and their pricing might start below $29 per provider, per month. Mid-tier plans typically cover everything an entry-level plan offers, plus advanced functionality such as patient scheduling and medical billing. Their prices (per provider, per month) tend to start in the double digits and go all the way into the thousands. Finally, high-end plans include additional premium features such as ePrescribing and telemedicine, and their per-provider, per-month pricing ranges from as low as $39 to $15,600+.
Buyers seek five features most often in medical software
When we asked buyers what functionalities they were looking for to manage their business’s core medical needs, a specific set of five core medical features emerged as crucial, especially for family medicine, psychiatry, medical spa, physical therapy, and chiropractic specialties.
Our research backed by advisor interactions indicates that one-fourth of the buyers (24%) request the below medical applications:

Electronic medical records or electronic health record (EHR) software assists in creating and storing digital patient records and tracking patient notes, demographics, histories, and medications. Features include e-prescribing, SOAP notes, E&M coding advice, and more. EMRs may also provide medical lab integration, device integration, tablet support, and voice recognition.
Patient scheduling automates the process of scheduling patient visits. Features include automated follow-ups, text message/phone/email reminders, and multi-location support. Typically offered with billing in a practice management suite.
Medical billing manages the creation of patient statements and submission of claims. Functions include coding, claims scrubbing, eligibility inquiry, electronic claim submission, payment posting, and reporting.
ePrescribing allows you to electronically generate and transmit a prescription order directly from a healthcare provider to a patient’s pharmacy of choice.
Telemedicine enables medical providers to diagnose or treat patients remotely using secure telecommunications tools such as video chats, phone, email, etc.
More resources for your software search
Whether you’re looking to buy new medical software or replace your existing tool, here are some additional resources to aid your software search:
Start with our interactive medical software directory to compare hundreds of products, filter your search by specific features, and read comprehensive reviews from SMB leaders.
Check out top-rated electronic medical records software based on usability and customer satisfaction in the 2023 electronic medical records software frontrunners.
Review our guide to healthcare software pricing models and medical buyers guide to compare tools and better understand the market.
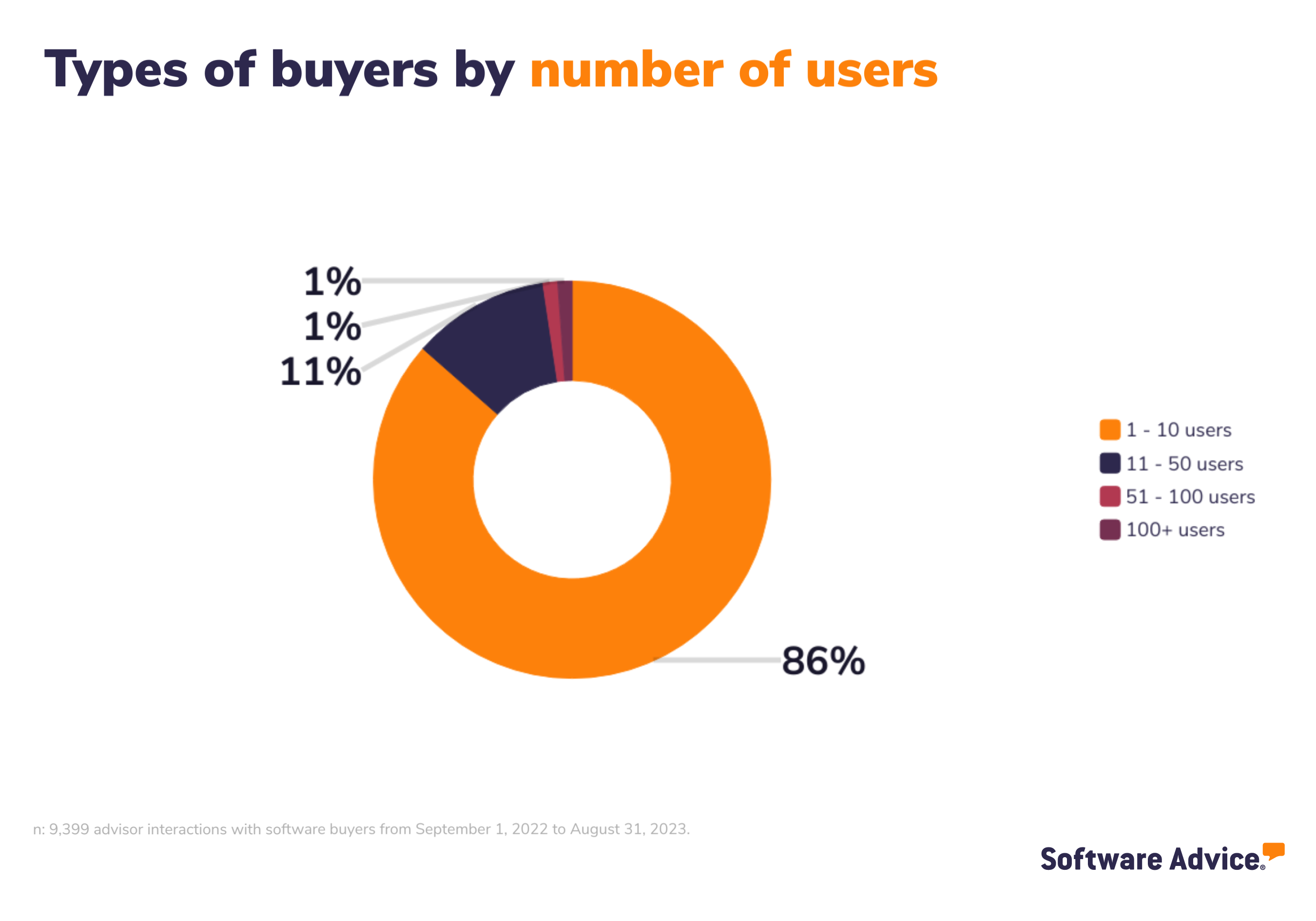
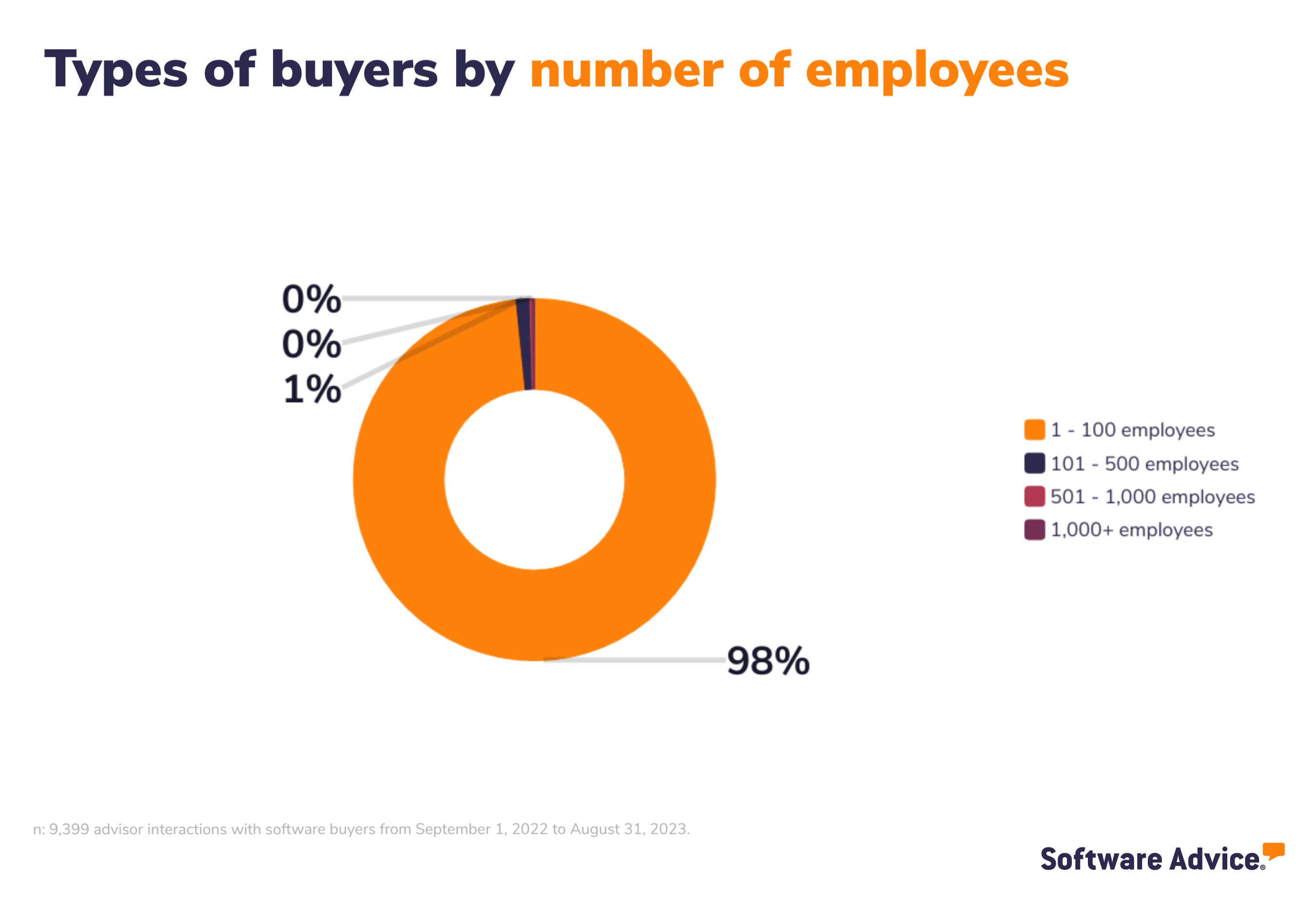
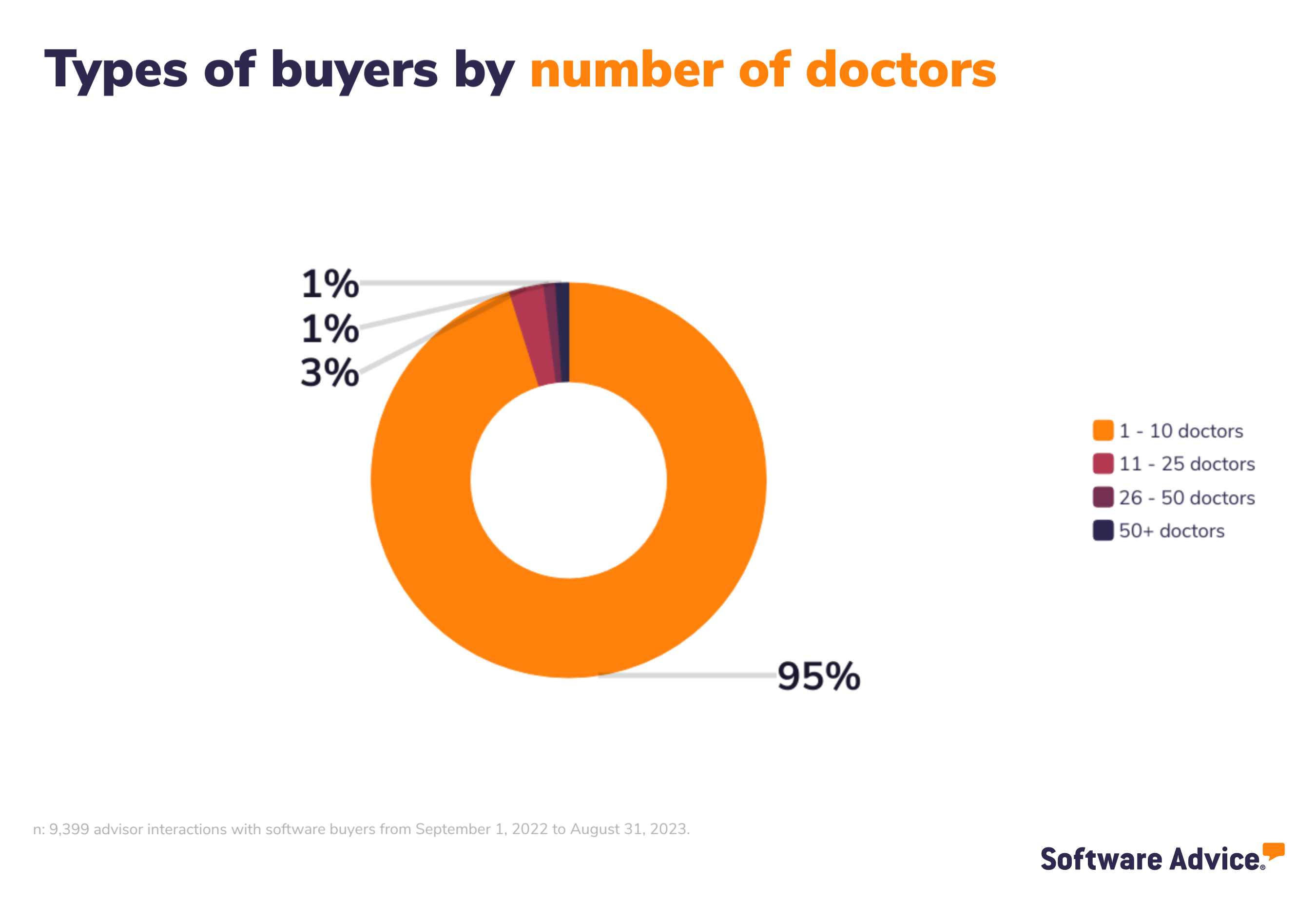
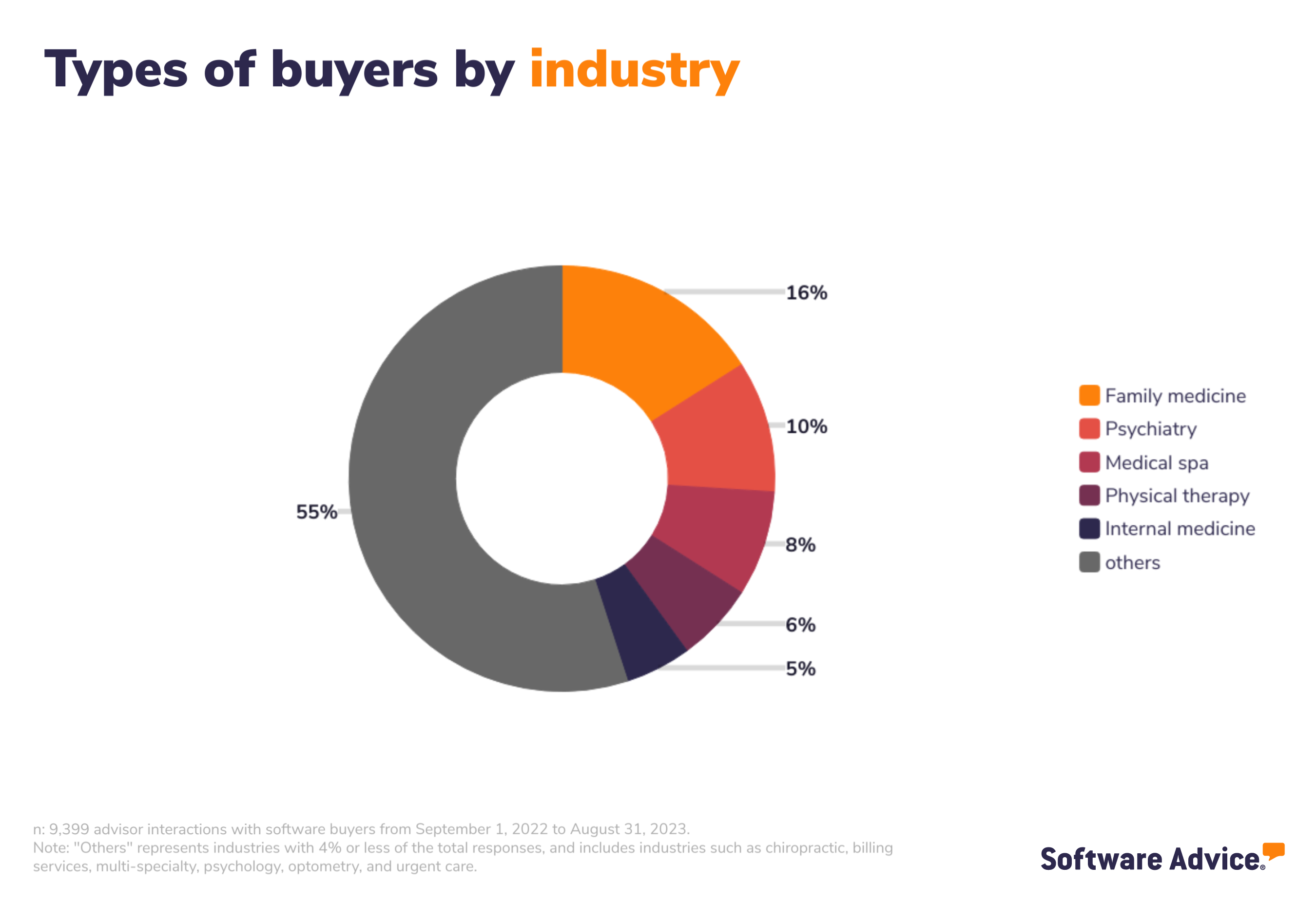
Buyer demographics
The buyers we interacted with are largely small businesses and below you’ll find the demographics of the buyers so you can see the size and type of businesses, from annual revenue to industry.
Survey methodology
Software buyers analysis methodology
Findings are based on data from conversations that Software Advice’s advisor team has daily with software buyers seeking guidance on purchase decisions. The data used to create this report is based on interactions with small-to-midsize businesses seeking medical tools. For this report, we analyzed approximately 9,399 phone interactions from September 1, 2022, to August 31, 2023.
The findings of this report represent buyers who contacted Software Advice and may not be indicative of the market as a whole. Data points are rounded to the nearest whole number.
Survey methodology
*Software Advice’s 2023 SMB Software Buying Trends Survey was conducted online from August 2022 to October 2022 among 1,513 respondents from the U.S., U.K., Canada, Australia, and France and from SMBs with revenue less than $1 billion and 2-999 employee size.
Respondents were screened for their involvement in software purchasing decisions and those who were a leader/ member of the group or had significant influence qualified for the study.