Best Practices for Telemedicine Implementation
As a response to the global pandemic, thousands of hospitals and independent medical practices have had to quickly purchase and deploy new telemedicine services to continue treating patients remotely.
A recent global SERMO survey of over 1,000 healthcare professionals found that the U.S. outpaced Europe and Asia in using telemedicine for remote treatment during the outbreak.
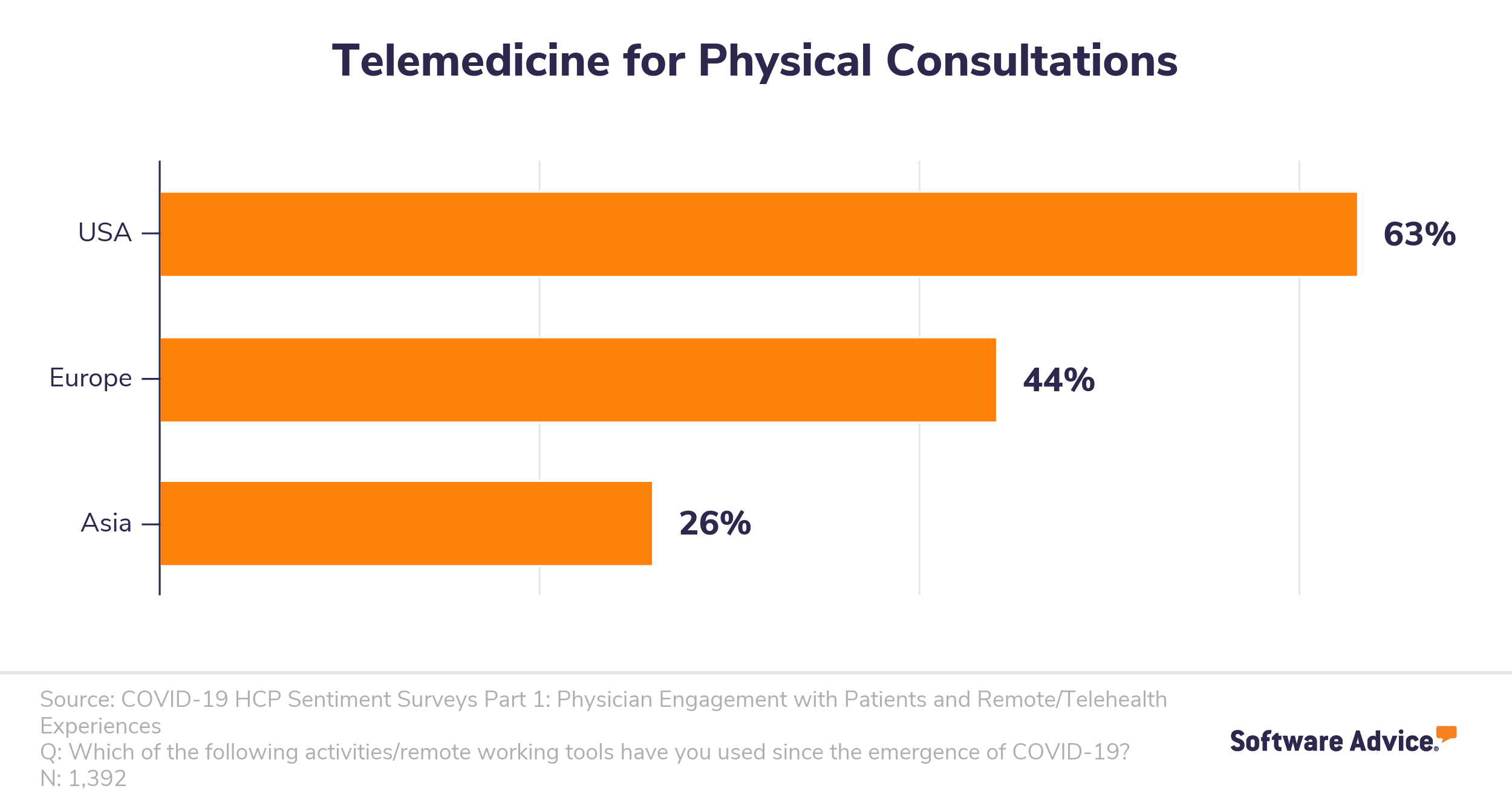
With this many practices in the U.S. implementing new telemedicine tools and systems, there are bound to be some mistakes in deployment. To help you avoid them, we’ve compiled this guide to all the best practices for implementation, from training to marketing, for your new telemedicine software.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
Training staff on using new telemedicine tools
Marketing new telemedicine services to patients
Maintaining compliance with telemedicine consultations
More telemedicine implementation resources
Training staff on using new telemedicine tools
In the same SERMO survey, researchers found that of the healthcare professionals (HCPs) using telemedicine for physical consultations, almost half (47%) are doing so for the very first time.

With that many doctors and staff having no prior experience with telemedicine, you have to put first things first; you can’t start using a new software system until you and your team know how.
If you’ve followed our recommendations for researching telemedicine providers and choosing the right one, you’ll have discussed customer support and training materials provided by your chosen vendor. Here is where you want to lean heavily on the provider for support. They’ll provide their own information and best practices for effective and secure telemedicine use, which you and your team can then build on.
The first step will be to arrange a training session led by your telemedicine provider’s team to introduce your staff to the software and tools. You’ll want to record this session to refer back to later.
Once the team has been introduced to the software and begun exploring it, they’ll likely have questions. This is a good opportunity to gather those questions and their answers to create a FAQ resource for current and future staff.
Action item: Provide an abundance of resources. Find a place that is secure and easily accessible to store hard or digital copies of training sessions, FAQs, security protocols, and any other tips and tricks for use, then make sure your staff knows this is the first place they can check when they have any questions about using your new telemedicine system.
Marketing new telemedicine services to patients
Once your staff is comfortable using the new telemedicine system and following best practices, you’ll need to bring your patients on board. This step involves some marketing and a whole lot of communicating, so hopefully you have a solid patient portal or outreach system in place to make sharing information with patients easy.
Fortunately, we know from our annual telemedicine patient survey that it’s likely your patients will be very excited by their new remote care options. In our most recent survey from February 2020, we learned that 84% of patients prefer doctors who offer telemedicine over those who don’t.
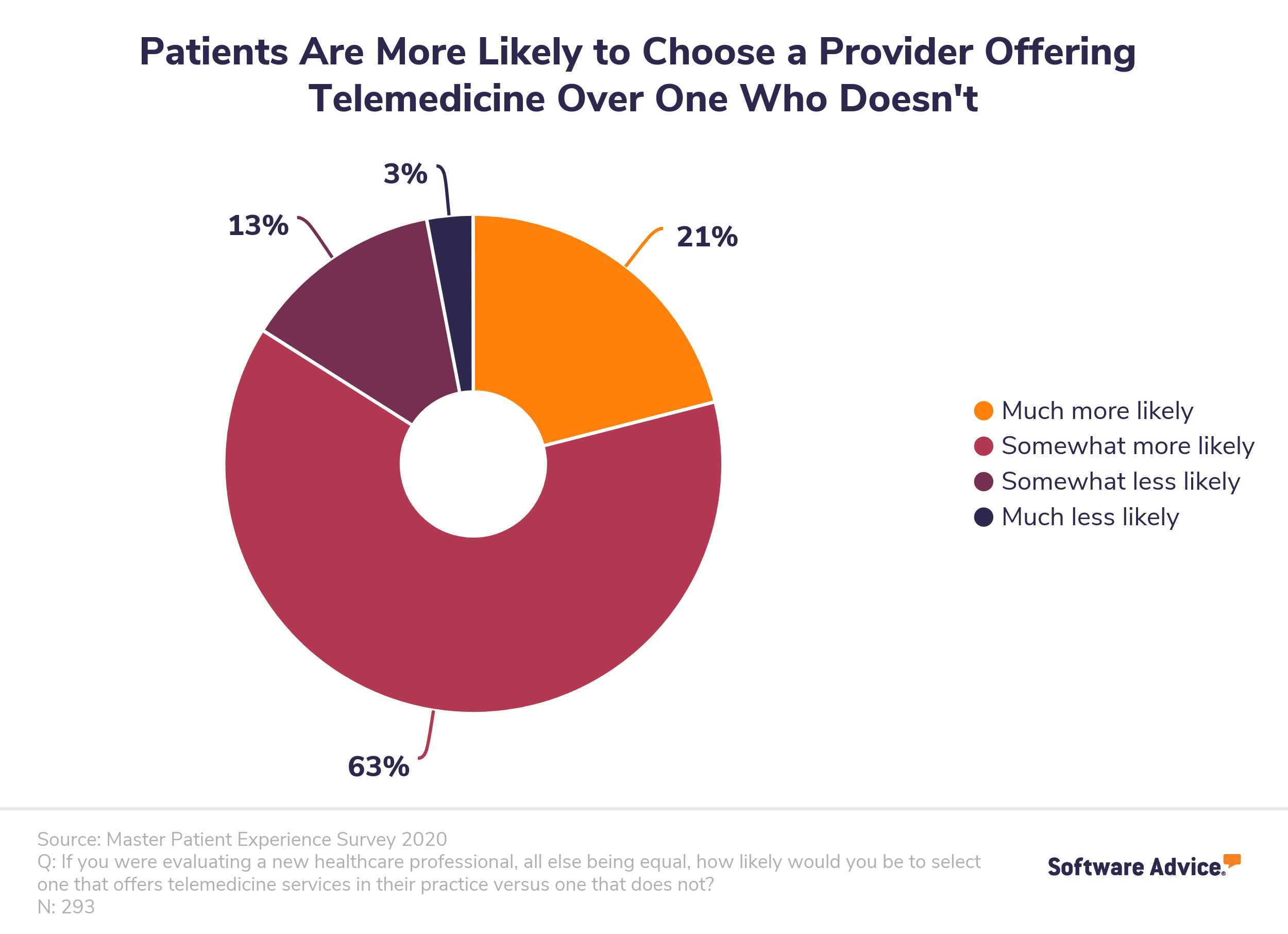
Start by sending out a mass email announcing your new telemedicine services and detailing which features you’ll be offering. Include the following information and resources in your notification:
The benefits of telemedicine for patients.
Simple instructions for getting started, including registration information, how to schedule remote consultations, and what tools they’ll need to participate (e.g., a webcam).
Access to resources such as patient FAQs as well as a way to reach out with questions and get support.
To get started, you can download our telemedicine notification template and edit it to meet your specifications. It’s also a good idea to collect signed patient consent forms along with other intake paperwork. Find a downloadable template for that form here.
Action item: Send out an email or message via patient portal announcing your new telemedicine system as well as resources that patients can access for registering and using the new tools.
Maintaining compliance with telemedicine consultations
Finally, as with any medical software, privacy and compliance are key factors in a smooth and successful implementation process. However, understanding all of the regulations and requirements around telemedicine could prove tricky. HIPAA and Medicare policies have recently been adjusted to make telemedicine more accessible, but it’s unclear how temporary or permanent those changes will be.
Additionally, several official organizations, including the FBI, have issued warnings around increased COVID-19 fraud schemes and targeted hacking attempts, and practices are being cautioned against rushing through telemedicine implementation as it could open them up to security breaches.
Digital healthcare has been plagued by several large-scale and high-profile data breaches over the years, and there’s no evidence that this is going to let up.
Proving to patients that your new telemedicine platform is secure will be critical for gaining patient buy-in early. According to George Jackson Jr., a senior principal consultant at healthcare cyber-risk management firm Clearwater, “Cybersecurity issues like hacking can adversely impact patients’ or providers’ level of willingness to trust telehealth. Digital health care has been plagued by several large-scale and high-profile data breaches over the years, and there’s no evidence that this is going to let up.”
In order to ensure privacy and security are maintained, it’s a good idea to follow the normal HIPAA best practices for telemedicine use. They include:
Only allowing authorized users to access electronic protected health information (PHI). This could include using tools such as multi-factor authentication for identity verification.
Using a secure communication platform to send and receive electronic PHI. Using a HIPAA-verified telemedicine platform may not be enough here. You may also consider adopting a virtual private network (VPN) that enables continuous endpoint posture checking to ensure data is protected both on your end and on your patients’ ends.
Implementing a monitoring system to audit all communications containing PHI. These systems should be equipped with key security features, such as the ability to remotely delete data and automatic log-off after a certain period of inactivity.
Action item: Check for HIPAA compliance before selecting a telemedicine provider. Then continue to monitor telehealth regulation changes and adjust usage accordingly.
More telemedicine implementation resources
If you’re looking for more information to help you in your telemedicine adoption journey, you may find the following research reports valuable:
What You Need to Know About Telemedicine in the World of COVID-19
A Conversation About the Applications and Benefits of Telemedicine in Addressing COVID-19
How Telemedicine Requirements Have Changed to Address COVID-19
If you’re still searching for the right telemedicine platform for your practice, reach out to our team of medical software advisors to discuss your software options and receive a list of products that meet your needs.