Find the best Reporting Tools
Compare Products
Showing 1 - 20 of 479 products
Sort by
Reviews: Sorts listings by the number of user reviews we have published, greatest to least.
Sponsored: Sorts listings by software vendors running active bidding campaigns, from the highest to lowest bid. Vendors who have paid for placement have a ‘Visit Website’ button, whereas unpaid vendors have a ‘Learn More’ button.
Avg Rating: Sorts listings by overall star rating based on user reviews, highest to lowest.
A to Z: Sorts listings by product name from A to Z.
Funnel
Funnel
Funnel is the leading marketing data hub designed to help marketing teams own their performance. With Funnel, marketers connect data from any marketing platform; store, organize, and share it with any visualization tool or data ...Read more about Funnel
Paladin Point of Sale and Inventory Management
Paladin Point of Sale and Inventory Management
For over 40 years, Paladin Data Corp. has been helping independent retail businesses run better. Paladin point of sale (POS) and inventory management software automates time-consuming inventory chores and provides business owners ...Read more about Paladin Point of Sale and Inventory Management
Asana
Asana
Asana is a comprehensive project management tool that offers a range of technical features to streamline workflows and enhance collaboration within teams. With its user-friendly interface and robust capabilities, Asana provides or...Read more about Asana
ShipCompliant
ShipCompliant
ShipCompliant is a cloud-based compliance and distribution management platform that provides various solutions for breweries, wineries, distilleries, importers and retailers. Key features include registration management, delivery ...Read more about ShipCompliant
AchieveIt
AchieveIt
AchieveIt is a cloud-based solution designed to help medium to large organizations in healthcare, government, utilities, enterprise, education, and more organize and integrate multiple plans, progress updates, and reports in a cen...Read more about AchieveIt
Angles Enterprise for SAP
Angles Enterprise for SAP
Your SAP enterprise resource planning (ERP) software has a wealth of data. But its complex nature makes it difficult for your teams to access, understand, and use the data efficiently and productively. Without data insights, you l...Read more about Angles Enterprise for SAP
Jet Reports
Jet Reports
Jet Reports is a flexible financial and business reporting solution running inside of Excel and on the Web. From advanced business reports to sophisticated financial statements, business users can create reports in Excel with no e...Read more about Jet Reports
Spreadsheet Server
Spreadsheet Server
Spreadsheet Server is a modular-based reporting solution that automatically pulls your live ERP data directly into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The solution allows users to generate reports from live data within Excel, leveragi...Read more about Spreadsheet Server
Wands for SAP
Wands for SAP
Wands for SAP empowers finance teams to create their own reports and to take advantage of a solution that is purpose-built to meet their reporting needs. Features include - - Cost Center Analysis - Budget-to-Actuals Variance - C...Read more about Wands for SAP
Vizlib
Vizlib
Vizlib is a data analysis and visualization software designed to help businesses across healthcare, life science, manufacturing, and other sectors streamline visual analytics and collaboration operations. One of its modules - Self...Read more about Vizlib
dReveal
dReveal
dReveal is a powerful, white-label, seamlessly embedded, and easily integrated reporting and dashboard solution, resulting from 20+ years of design development. Thousands of users, from thousands of companies, benefit from using...Read more about dReveal
Informer
Informer
Entrinsik Informer is a business intelligence tool that is designed for business and IT professionals. Key features include a dashboard, data scheduling and analysis and report generation. Entrinsik Informer allows users to e...Read more about Informer
Logi Symphony
Logi Symphony
Logi Symphony is a highly flexible browser-based embedded business intelligence (BI) and analytics platform. Software teams use Logi Symphony to embed interactive managed dashboards, self-service dashboards, and pixel-perfect repo...Read more about Logi Symphony
Grow
Grow
Grow is a cloud-based, business analytics and reporting solution suitable for small to midsize organizations. The solution allows users to create customizable dashboards for monitoring business workflows and key activities. Grow...Read more about Grow
IRIS CARBON
IRIS CARBON
IRIS CARBON is a disclosure management solution. It helps companies simplify financial reporting and regulatory compliance. IRIS CARBON caters to public companies, private companies, and accounting firms. IRIS CARBON offers key f...Read more about IRIS CARBON
Axiom Software
Axiom Software
Syntellis Performance Solutions provides innovative enterprise performance management software, data and analytics solutions for healthcare, higher education and financial institutions. Syntellis’ solutions include Axiom and Conne...Read more about Axiom Software
BOARD
BOARD
FrontRunners 2024
Board is the Intelligent Planning Platform that offers smarter planning, actionable insights and better outcomes for more than 2,000 companies worldwide. Board allows leading enterprises to discover crucial insights which drive bu...Read more about BOARD
CRM Analytics
CRM Analytics
Salesforce Analytics Cloud, also known as Wave Analytics, is a cloud-based business intelligence (BI) system that provides an interactive platform to access and share business trends. The software provides data insights and helps ...Read more about CRM Analytics
AgencyAnalytics
AgencyAnalytics
AgencyAnalytics is the only marketing platform built specifically for agencies. Save time, boost revenue and impress clients with a brandable cloud based reporting platform that lets you monitor and report on all of your clients' ...Read more about AgencyAnalytics
AD FastReporter
AD FastReporter
AD FastReporter is an on-premise active directory reporting tool which caters to the needs of IT professionals across multiple geographies. Key features include automation of reporting tasks, report storage and built-in report for...Read more about AD FastReporter
Popular Comparisons
Buyers Guide
Last Updated: March 16, 2023Generating business reports can be a giant headache. Many companies work with multiple disconnected sources of data and, therefore, struggle to analyze business performance in a way that's efficient and actionable.
This is where reporting tools come in. Reporting tools are used to create dashboards, data visualizations, charts and more so companies can more easily gauge business performance.
This guide will explain the types of reporting tools available, their benefits and key considerations for buyers making a purchase decision.
Here's what we'll cover:
Common Types of Reporting Tools
What Are Reporting Tools?
Reporting tools gather key data from multiple sources and consolidate it. From the collected business performance data, companies can identify trends, patterns and areas for improvement.
Many customer relationship management (CRM) systems offer some reporting functionality, as do many enterprise resource planning (ERP), marketing and sales software solutions. There are also many standalone reporting tools to choose from.
Common Types of Reporting Tools
Buyers purchase reporting tools for many reasons:
They have too many employees for their existing reporting tools or methods
Their current tools can no longer handle the amount of data the organization collects
Their existing methods are slow, cumbersome and inaccurate
Their current tools are only usable by IT staff, i.e., not accessible
While different solutions vary, there are a number of reporting solutions that address the above pain points. Below are the most common types:
Dashboard software | Helps organizations focus on the metrics that are most important to their operations. Think of a dashboard as a display of the current overall status of your business. |
Data visualization software | Offers graphical representations of data via simple user interfaces. Gives users a more insightful way to look at data that is often more digestible for those who feel overwhelmed by reports heavy on figures and text. |
Scorecarding tools | A performance management tool to compare strategic goals with results by attaching a numerical weight to performance and mapping progress toward goals. |
Ad-hoc report writers | Help users design and generate custom, ad-hoc reports. This is especially helpful for organizations that frequently modify their analyses and need to generate new reports quickly. |
Benefits of Reporting Tools
There are many benefits to using reporting tools, including:
Visibility of key metrics. Users have immediate access to the information they need to answer critical, real-time questions. This improves and speeds decision making.
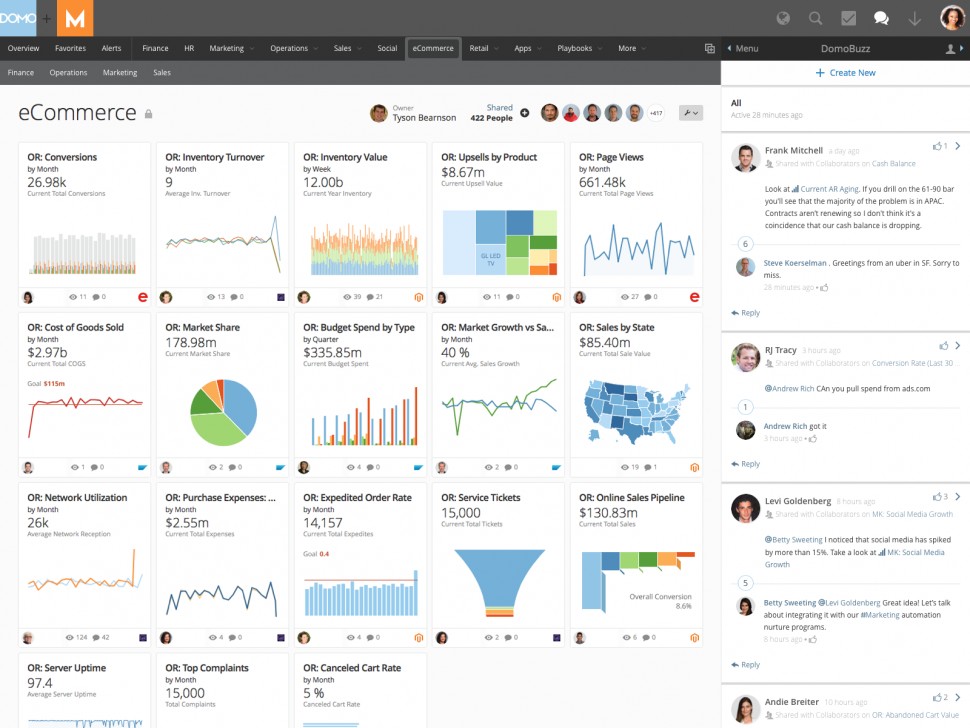
Domo's Card Builder interprets your data and suggests how to visualize it. This helps users quickly access the most important and critical data for their business.
Improved accessibility. In the past, only team members with technical skills could build and access analytics reports. Today, reporting tools make it easy for anyone to instantly create reports and share data.
Key Considerations
A good reporting tool should align with your company’s strategy and goals. It should also offer the following characteristics:
Ease-of-use. If your reporting tool is complicated to use, or even looks like it might be, employees will balk at the idea of using it, or simply give up. Look for reporting tools that are easy to learn with intuitive features and vendors that offer tutorials. To get a sense for this, check out reviews from real users when evaluating your options.
Sisense offers “getting started” tutorials to help new users get up to speed.
Easy implementation. To avoid a lengthy implementation or one that requires technical expertise, look for software that is easy to get up and running. This saves your IT department the burden of a time-consuming, cumbersome implementation process and ensures you’ll be able to start using your reporting tool right away.
What Type of Buyer Are You?
Reporting tools are used in a wide variety of fields by many types of users. Some of the most common include:
Business and IT analysts. Analysts need to create data visualizations on dashboards that they can embed in different applications. These are buyers looking for tools that allow them to fetch unstructured data from different sources and create customized dashboards for their colleagues, partners and clients. The ideal reporting tool should offer back-end support and integration capabilities that make pulling reports from different systems and databases easy.
Consultants and customer service managers. Reporting tools should enable consultants and customer service managers to create interactive dashboards rather than just data-driven "Excel-based" reports. These buyers are looking for tools that help them seamlessly add customer details or feedback collected from surveys and forums into dashboards. Once that’s done, their clients should be able to interact with the data and drill down to perform further analysis.
Department heads and business managers. A reporting tool that caters to department managers must have integration capabilities with different business applications. Managers need to be able to share data dashboards with colleagues and other stakeholders who use different systems. These could range from human resource management (HRM) and CRM to ERP software and many other tools. Therefore, these users need a reporting solution that comes with advanced integration capabilities. Besides this, such buyers are looking for solutions that offer easy customization options and allow quick access to key business metrics.
Software providers. Software vendors look for reporting tools that integrate with specific functionalities of their software, such as a knowledge base, custom portal etc. At times, they may even decide not to build a native reporting tool and instead embed a third-party reporting dashboard within their solution. These buyers are looking for advanced integration capabilities and white label options.
Nontechnical business users. Professionals in traditionally nontechnical departments, such as sales or customer support, require dashboards where they can view data in a single click. These buyers need reporting tools with interactive dashboards that allow them to drill down further into reports, such as product sales, consumer behavior, budgets and more.
Market Predictions
Gartner’s ''Market Guide for Enterprise-Reporting-Based Platforms'' (content available to Gartner clients) states: ''By 2020, 80% of all enterprise reporting will be based on modern BI and analytics platforms; the remaining 20% will still be on IT-centric reporting-based platforms because the risk to change outweighs value.''
Forbes Insights, in association with Qlik, conducted a global survey of 437 senior executives, which revealed that four out of five organizations (81 percent) experienced ''very significant business benefits from their BI programs.''







