CRM Roadmap 2.0: The Better Path to Sales Success
Customer relationship management (CRM) software is among the most complicated systems that you’re likely to buy for your small to midsize business (SMB). That’s why you need a plan in place to get that software up and running—a CRM roadmap.
But not all maps are created equal. Maybe yours ends in the middle of the highway. Or it leads you into a lake.
Without a well-considered CRM roadmap, your SMB is far more likely to face an extremely costly implementation failure and lose money on CRM capabilities it’s not taking advantage of.
You need to create a bucketed CRM roadmap to make sure you’re specifically investing in unique and new features that will keep your SMB competitive.
This article will explain what buckets to focus on and help you develop that roadmap so you can properly plan for when and how you’ll implement different important CRM software functions!
Here’s what we’ll cover:
The Secret to Roadmap Success: Targeted Bucketing
Roadmap in Action: Create Your Own With This Template
How Do I Get The Most Out Of My CRM Roadmap?
What Is a CRM Roadmap?
In today’s small business world, your CRM roadmap will guide how and when you implement and onboard new software systems to meet your needs.
A “CRM roadmap” isn’t literally a map. But it’s like a map in that it’s a tool you can use to guide your SMB towards its objective of meeting and exceeding your customers’ expectations and your own sales goals.
With your roadmap, you will clearly know when, where and how you plan to implement strategies and technologies to follow through with the key tenets of CRM. These include keeping track of customer information and relationships, closing more sales leads, providing world-class customer service and more.
What might cause a faulty map that hurts your business? A bad CRM roadmap might fail to:
Align with your overall CRM strategy
Take all necessary stakeholders into consideration
Allot the time needed to onboard employees
Consider both implementation costs and ongoing costs
Account for future business and technology growth
A good CRM roadmap, then, must follow the above best practices. We will discuss the best way to do this in the following section.
The Secret to Roadmap Success: Targeted Bucketing
Our approach to a CRM roadmap is taken from a strategic innovation developed by Gartner analysts in the report “What Is Gartner’s Pace-Layered Application Strategy and Why Should You Use It?” (available to Gartner subscribers).
The idea of a “pace-layered approach” is tailored to enterprise-level businesses, so your SMB can bypass much of the jargon of that report and focus instead on one simple process—targeted bucketing.
To create your roadmap, you first need to organize your CRM needs into three distinct buckets: “common features,” “unique features” and “new features.”

The same need may be classified differently in your company than it is in another, based on its use and its relationship to your respective business models. But let’s look in more detail at what makes up each bucket.

Common features are those capabilities or functions that have a clear focus on operational efficiency and/or standardization. In essence, they’re the features that you use day in and day out to run your SMB.
Here’s how you can identify which software functions are your common features:
The capabilities of the solution are essential to core business processes within the organization, even if they do not provide competitive differentiation.
The function of the solution is universal, such that most vendors provide similar functionality.
The solution can be easily implemented completely “out of the box,” with little customization or configuration, aided by best-practice templates.
For CRM software, common features may include:
Stores customer contact information. | |
Helps organizations automate the movement and tracking of leads through the sales life cycle from acquisition to conversion, helping to increase efficiency and qualification and conversion rates. | |
Helps sales teams to manage accounts, leads, opportunities and customer interactions, and helps sales managers generate more accurate forecasts and gain better insight into opportunities. | |
Provides cost estimates for custom orders, often in the context of a built-to-order manufacturing operation. |

Unique features are those capabilities/functions that enable distinctive company processes or industry-specific capabilities. These are the features you use to give you a competitive advantage over similar SMBs in your market.
Here’s how you can identify which software functions are your unique features:
Those solutions reflect the best business process practices of your industry and can be configured to meet your specific business requirements.
There are third-party vendor solutions purpose-built for automating this process.
The technology helps you differentiate your processes by providing a competitive advantage, as most of your competitors have yet to adopt the capabilities.
The feature has prebuilt data and application connectors to your sales force automation or CRM feature.
For CRM software, common SMB unique features include:
Helps companies engage with social media users by publishing content to social media platforms, locating social media users or conversations and measuring the relative success of social media marketing campaigns. | |
Tracks the activities of sales teams in order to provide reports and run diagnostic analytics that can suggest next best actions. | |
Provides infrastructure for organizing company documents by managing digital assets and media files. |

New features are new business capabilities that are built on an ad hoc basis to address emerging business requirements and/or business opportunities. These are the experimental features used for testing new ideas and identifying your SMB’s next competitive advantage.
Here’s how you can identify which software functions are your new features:
The capabilities of the feature are completely new to your organization or your industry.
The capabilities are so targeted that they are relevant to only a subsegment of sales users or departments.
The technology is only available from small, third-party vendors.
The capabilities of the feature seem risky, either because of the expense or because the technology is not yet mature.
For CRM software, SMB new features include:
Streamlines the mobile CRM/sales automation experience for on-the-go users in the field. | |
Offers social media engagement insights and analysis to help you identify when and where to create and respond to posts. | |
Improves sales performance and productivity by providing insight into pipeline health and how best to win opportunities. |
Roadmap in Action: Create Your Own With This Template
Now that you’re familiar with all the elements of our new and improved CRM roadmap strategy, you’re ready to create a new, bucketed CRM roadmap!
Your CRM roadmap should include the common, unique and new features you’ll be implementing, an ETA for implementation and the expected cost once implemented.
Here’s an example of what your roadmap might look like:
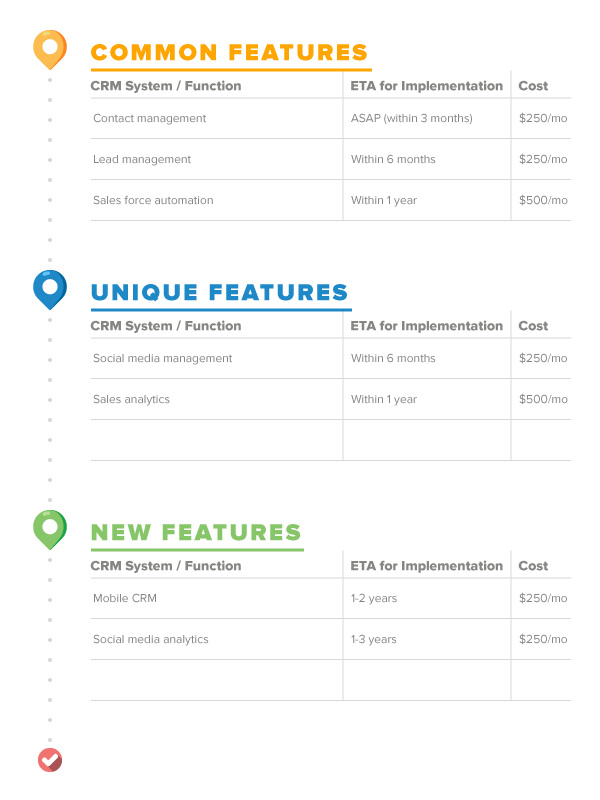
Though this may seem daunting, in practice it’s really quite simple. It can be divided up into the following step-by-step process that you and stakeholders across your company should work on together:
Classify common features and unique features: Review the features and functionality of CRM software (either from your current vendor or from vendors from whom you may be considering purchasing new/updated software) and bucket each one as either a common feature or a unique feature.
Identify new features: Consider features and functionality that might prove helpful to your business model but are not provided by most CRM vendors. Features such as mobile solutions, artificial intelligence, predictive analytics etc. may give you a competitive advantage. List what potential new features interests you the most.
Strategize when and how to implement new software: Review your list of common features, unique features and new features. Consider which features you are currently using and which ones you should be using, then strategize as to which of the latter you are going to put into place and in what order.
Download our template and create your roadmap: You’ll need an accessible document which can be regularly updated. It should clearly map out which unique features and new features you are going to begin implementing and when you plan to do so. It should include the ETA for implementation and an approximate cost for each feature. We’ve included our template below.
Download our CRM Roadmap template
How Do I Get The Most Out Of My CRM Roadmap?
In the report “Best Practices for Developing a Pace-Layered Roadmap for CRM Sales Applications” (available to Gartner subscribers), Gartner provides guidance on how you can implement your roadmap once you have it in writing:
Have a handful of new features active with pilot groups at all times.
Avoid software saturation; only deploy new features to the entire organization if they produce efficiency or effectiveness gains. To rapidly convert new features to unique features, document and socialize the best practices learned from pilot groups.
Plan for unique features gradually to become common features, because your competitors will adopt similar technologies and capabilities in their own CRM sales implementations.
A well thought-out, bucketed CRM roadmap will thus give you a cohesive plan to make sure you’re utilizing all of the features and functions of your CRM in order to maintain a full competitive advantage and remain ahead of the curve when it comes to new CRM/sales processes.
And finally, once your implementation is mapped out and underway, uncover the hidden features and functionalities of your CRM system by reading up on some helpful CRM hacks and by learning which CRM features you might be paying for unnecessarily.