3 Types of Telemedicine and How They Each Improve Patient Experience
Telemedicine has been around for a long time, but recent circumstances have caused its adoption rates and popularity to skyrocket.
For many practices and patients, this is a new technology that they must now learn how to engage with in order to continue managing their care safely. To that end, it’s worth exploring the different types of telemedicine and how each can be used to address specific patient needs.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
Telemedicine isn’t going away
Before we get into the different types of telemedicine, it’s important to understand the growing importance of telemedicine software.
In February of 2020, we ran a patient survey(#foot note) to gather data around what technologies patients have experience using and their general sentiments around the use of technology to improve delivery of care. We found that, at the time of the survey, a majority of patients had never used telemedicine to consult with a medical provider remotely.
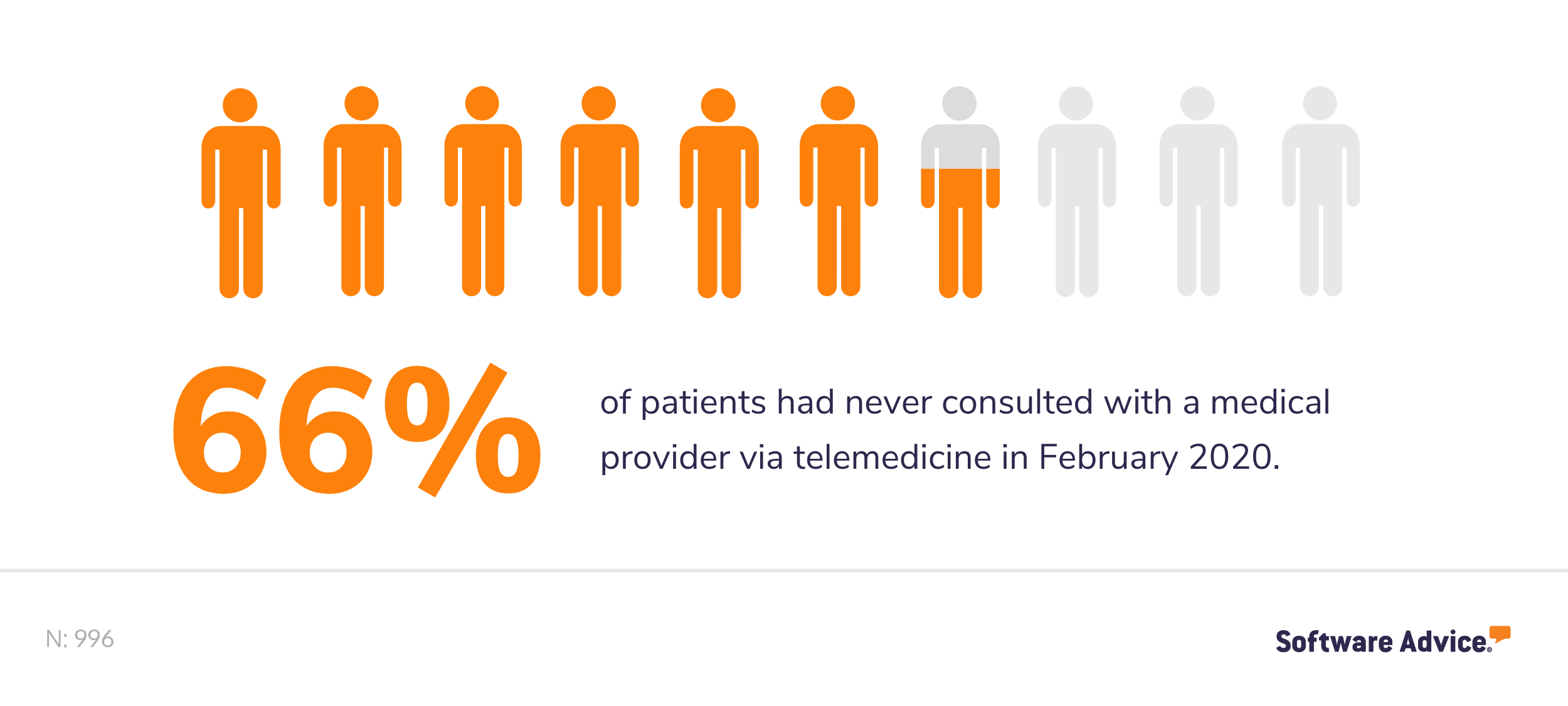
As you can imagine with the recent pandemic and rapid uptick in telemedicine adoption, that number has gone down dramatically.
According to a Sermo survey conducted in April 2020, 63% of healthcare professionals have used telemedicine to consult with patients since the outbreak, and an average 57% of patients were being treated via telemedicine globally at the height of the pandemic.
With these data points in mind, it’s not a huge leap to assume telemedicine adoption rates will continue to rise in independent practices.
That said, there is still a question of how patients are adapting to remote care technology and how to best utilize these software platforms to improve care, which brings us to the point of understanding different types of telemedicine and how each can best be utilized to serve patients depending on the practice.
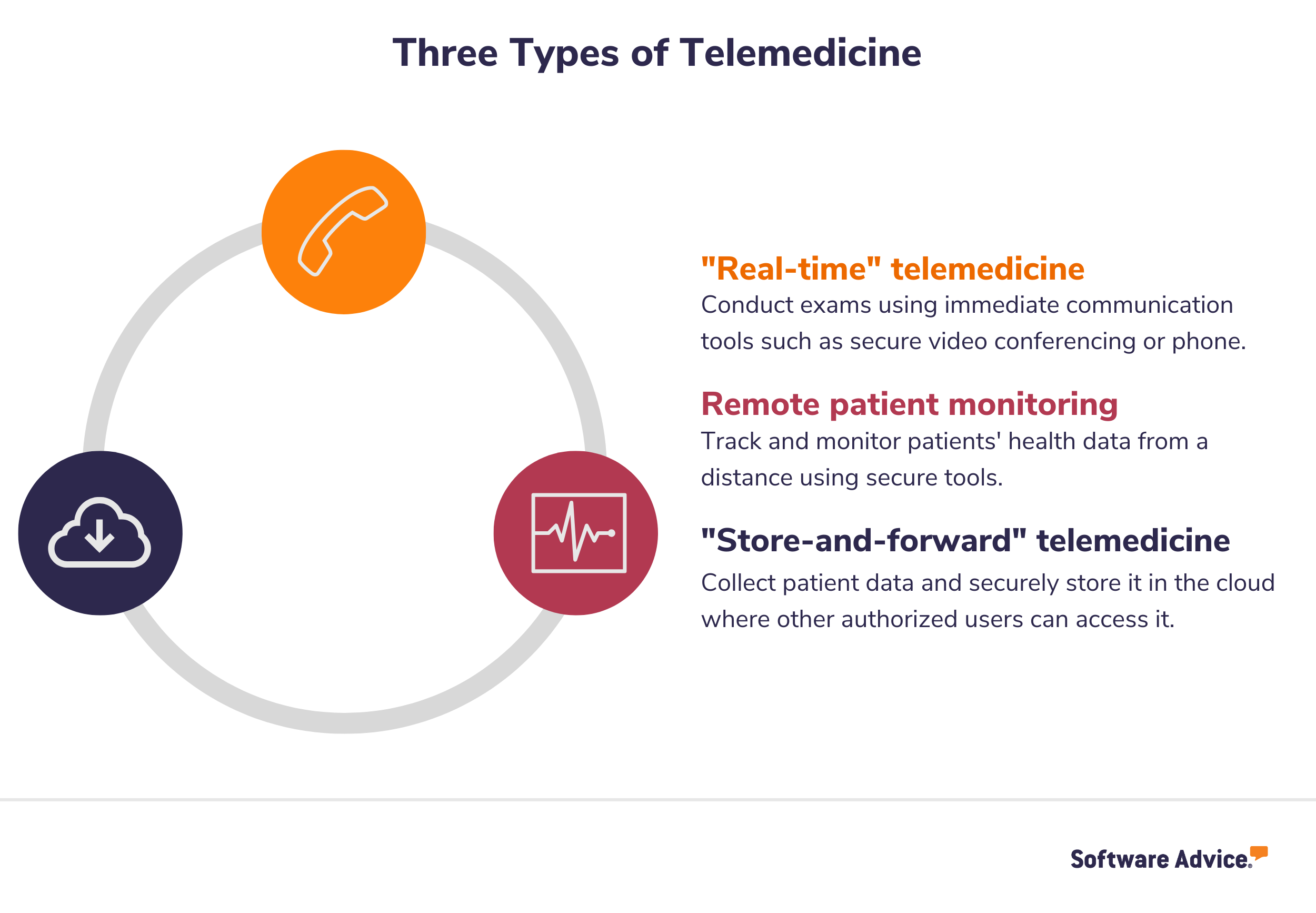
Real-time telemedicine replaces in-person appointments
Most people’s perception of telemedicine falls under the category of “real-time” telemedicine, as it is the most common type. Simply put, real-time, or live telemedicine, is any software that enables medical providers and patients to consult with one another remotely in real time.
This type of telemedicine uses two-way communication tools such as video conferencing, live chat, or phone calls to conduct exams as if the doctor and patient were in the same room.
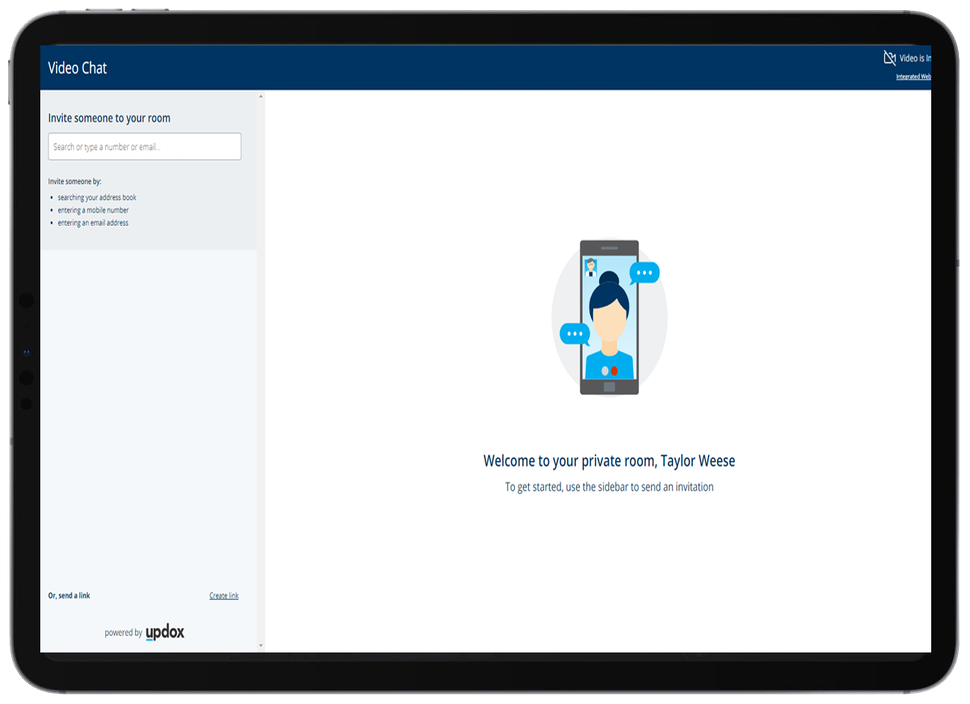
Live video chat feature in Updox telemedicine software
Obviously not all types of medical exams can be conducted via live telemedicine, as physical tests require physical contact. However, there are many consultations that are perfectly suited to take place remotely, such as screenings, general assessments, and behavioral therapy sessions.
The biggest benefit of real-time telemedicine is how it maintains the doctor-patient relationship without requiring either to leave their own homes or practices. It is convenient to all users and incredibly useful in protecting immunocompromised patients from exposure to dangerous contaminants when traveling to a doctor office.
Remote patient monitoring is well suited for chronic care
The next most common type of telemedicine is remote patient monitoring, which allows medical providers to track and monitor patients’ health data from a distance. This remote monitoring telemedicine is most often used to keep track of patients with chronic conditions in their homes, so those patients don’t have to make daily trips to see a medical provider in person.
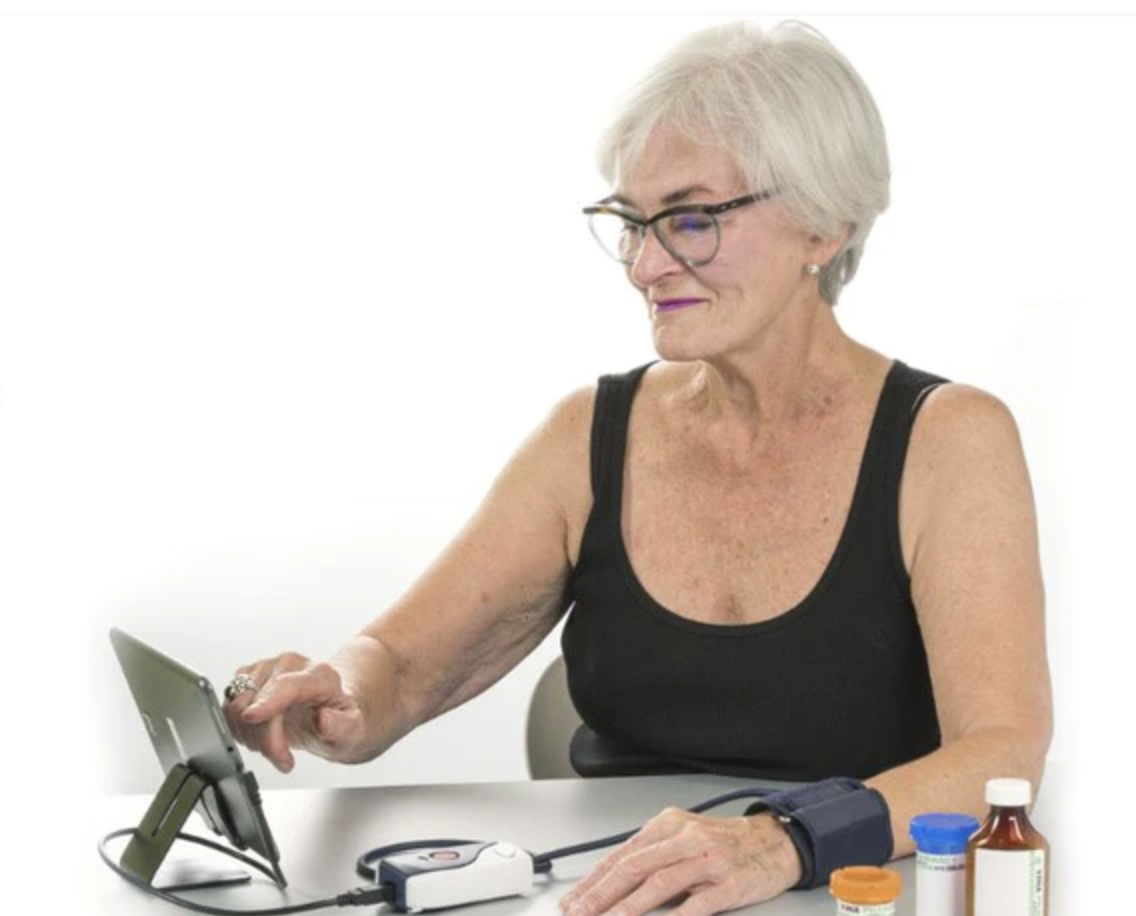

Remote patient monitoring tools offered within Cloud DX telemedicine software
Remote monitoring tools vastly improve the patient experience because they are able to collect patient health information while the patient is comfortably in their own home and then send that information to medical providers.
From there, providers can keep an eye on patients’ progress and receive alerts if any stats indicate declining conditions.
Again, remote monitoring telemedicine is not ideal for every type of patient—however, it is incredibly useful for gathering data such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen levels, and other vital signs that tell doctors how patients with chronic conditions such as heart disease, asthma, or diabetes are faring.
The biggest benefit of remote patient monitoring is that it provides those patients with chronic conditions more independence from making frequent physical trips to care facilities without sacrificing their quality of care.
Store-and-forward telemedicine allows for evidence-based care
Store-and-forward telemedicine, sometimes called asynchronous, is the opposite of real-time telemedicine in that it allows patient data to be gathered and then securely transferred to a secure cloud-based platform that other authorized users can then access at any time.
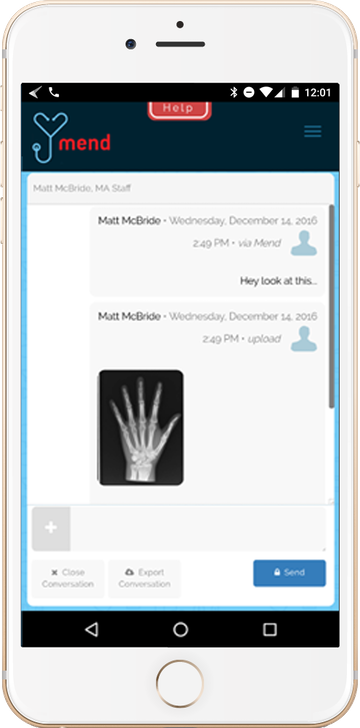
Medical image sharing feature in Mend telemedicine software
Asynchronous telemedicine and real-time telemedicine are often used in conjunction with one another to provide robust and thorough care.
Where real-time telemedicine is excellent at addressing timely concerns, store-and-forward telemedicine allows providers the time to carefully consider and analyze all of the patient information collected, identifying trends over time as well as immediate changes.
The biggest benefit of store-and-forward telemedicine is that by removing the time constraints of live telemedicine exams, it allows providers to apply evidence-based care practices to make more accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
Which type of telemedicine is best for you?
With a greater understanding of the three major types of telemedicine, you can now determine which is the best fit for your practice.
If you are a general practitioner:
Real-time telemedicine is your first choice. This type of telemedicine is best suited for conducting general exams. Unless your practice treats chronic patients, you won’t get much out of remote monitoring telemedicine tools. You may want to consider investing in asynchronous telemedicine if you intend to offer prolonged remote consultations.
If you are a specialist offering long-term care:
Remote monitoring is your best option. However, you could also benefit from real-time and store-and-forward telemedicine consultations as the current pandemic continues to threaten immunocompromised patients.
If you want to learn more about telemedicine software and which platforms will work for you, you may find these guides and reports helpful:
You can also speak to our medical software advisors for free to learn more about your telemedicine software options by scheduling a call or starting a live chat.
Methodology
1To find the data in the report referenced here, we surveyed over 1,000 patients in the United States. We used screening questions to narrow the number of respondents down to 990 with relevant histories and experiences. We worded the questions to ensure that each respondent fully understood their meaning and the topic at hand.
If you have comments or would like to obtain access to any of the charts included in this report, please contact lisa.hedges@gartner.com.
Note: The applications selected in this article are examples to show a feature in context and are not intended as endorsements or recommendations. They have been obtained from sources believed to be reliable at the time of publication.