Find the best E-Prescribing Software
Compare Products
Showing 1 - 20 of 58 products
Sort by
Reviews: Sorts listings by the number of user reviews we have published, greatest to least.
Sponsored: Sorts listings by software vendors running active bidding campaigns, from the highest to lowest bid. Vendors who have paid for placement have a ‘Visit Website’ button, whereas unpaid vendors have a ‘Learn More’ button.
Avg Rating: Sorts listings by overall star rating based on user reviews, highest to lowest.
A to Z: Sorts listings by product name from A to Z.
athenaOne
athenaOne
The athenaOne Suite which includes athenaCollector a revenue cycle management solution and athenaClinials an EHR (electronic health records) recently ranked #1 in 2023 Best in KLAS for athenaClinials Ambulatory EMR for 11-75 physi...Read more about athenaOne
RXNT
RXNT
RXNT’s cloud-based, ONC-certified medical software—Billing, Practice Management, EHR, and more—improves clinical outcomes & revenue cycle management. Simple, transparent pricing includes free setup and training, free data transfer...Read more about RXNT
DrChrono
DrChrono
DrChrono’s iPad and iPhone compatible EHR and medical billing platform allows medical practices and healthcare providers to manage patient intake, patient care, clinical charting, billing and revenue cycle management. It includes ...Read more about DrChrono
ChartLogic EHR
ChartLogic EHR
ChartLogic offers an ambulatory EHR suite that includes electronic medical record, practice management, revenue cycle management, e-prescribing and patient portal. The solution caters to primary care, surgical care and other compl...Read more about ChartLogic EHR
Talk with us for a free
15-minute consultationSoftware Advice is free because vendors pay us when they receive sales opportunities.
This allows us to provide comprehensive software lists and an advisor service at no cost to you.
This allows us to provide comprehensive software lists and an advisor service at no cost to you.
Meet Eric, a software expert who has helped 1,534 companies select the right product for their needs.
Talk with us for a free
15-minute consultationSoftware Advice is free because vendors pay us when they receive sales opportunities.
This allows us to provide comprehensive software lists and an advisor service at no cost to you.
This allows us to provide comprehensive software lists and an advisor service at no cost to you.
Tell us more about your business and an advisor will reach out with a list of software recommendations customized for your specific needs.
STEP 1 OF 4
How many doctors are in your organization?
Nexus EHR
Nexus EHR
Nexus EHR is an ONC Certified 2015 Edition Cures Update cloud-based ambulatory EHR and PM platform. It is designed for small to midsize practices and various specialties including orthopedics, neurology, podiatry, cardiology, gene...Read more about Nexus EHR
NewCrop
NewCrop
NewCrop is a comprehensive prescribing software solution that can be used with a wide variety of electronic medical systems. NewCrop is designed to integrate with any EMR or EHR system. NewCrop includes industry-leading functional...Read more about NewCrop
CharmHealth
CharmHealth
CharmHealth is a MU certified, cloud-based EHR, Practice Management and Medical Billing solution that helps healthcare organizations ranging from large multi-specialty groups to small independent medical offices function efficient...Read more about CharmHealth
NextGen Office
NextGen Office
NextGen Office is an award-winning, cloud-based, clinical and billing solution designed for smaller, independent practices (≤ 10 providers). This all-in-one, full-service solution includes specialty-specific EHR content, an easy-t...Read more about NextGen Office
DxScript
DxScript
DxScript is a HIPAA-compliant cloud-based application. It offers integration with EHR/EMR/PM systems at no cost or stand-alone, and is DEA-compliant and certified for EPCS in all 50 states. It includes Prescription Drug Monitori...Read more about DxScript
HARMONY Medical
HARMONY Medical
Harmony e/Notes is a hybrid integrated solution that offers functionalities for electronic medical records, practice management, billing and revenue cycle management. Specialities that the solution caters to include cardiology, ge...Read more about HARMONY Medical
DocVilla
DocVilla
DocVilla is a HIPAA-compliant Cloud-based software for medical practices. DocVilla offers integrated EHR (Electronic Health Records), EMR (Electronic Medical Records), Telemedicine, Electronic Prescriptions (eRx), EPCS (Electronic...Read more about DocVilla
iCare
iCare
iCare is the modern cloud-based EHR for health systems, clinics, and physician practices. iCare provides a unified Electronic Health Record for today's best healthcare providers. Easy to implement and easy to use, iCare’s flexib...Read more about iCare
Tebra
Tebra
Looking to harness the full power of the Tebra platform? Our practice success platform includes a certified electronic health record solution built to empower today’s providers with robust clinical charting, streamlined documentat...Read more about Tebra
Practice Fusion
Practice Fusion
Founded in 2005, Practice Fusion offers a cloud-based EHR that includes a suite of integrated features like charting, e-prescribing, patient scheduling, lab and imaging integration and more. Additionally, practices can qualify for...Read more about Practice Fusion
Pabau
Pabau
Pabau's all-in-one software is built to handle everything that clinics (both large and small) need to run smoothly. Forget spreadsheets, integrations, paper notes and scanning — do it all from one easy to use tool. - Save 12+ ...Read more about Pabau
Qualifacts Insync
Qualifacts Insync
Enhance patient care with InSync's fully integrated, easy-to-use, cloud-based healthcare IT solutions configured specifically to your practice and workflows. EHR, practice management, medical billing, telemedicine, e-prescribing a...Read more about Qualifacts Insync
Alleva
Alleva
Alleva's EMR software solution offers the latest technology to therapists, improves the quality of their work, and relieves stress. The intuitive, user-friendly platform eases the workflow for those providing care. The EMR dashbo...Read more about Alleva
Veradigm Practice Management
Veradigm Practice Management
Veradigm Practice Management (formerly Allscripts Practice Management) is a cloud-based solution designed to simplify and optimize the daily operations of physician practices. The platform offers a range of features, including sch...Read more about Veradigm Practice Management
MDToolbox-Rx
MDToolbox-Rx
MDToolbox-Rx is a cloud-based solution designed to help medical organizations of all sizes send electronic prescriptions to various pharmacies. A Surescripts and EPCS-certified solution, it enables users to access patient history ...Read more about MDToolbox-Rx
Intergy
Intergy
Intergy offers ambulatory practices a specialty-focused EHR and practice management solution that is both user-friendly and customizable. With Intergy’s tools, users can manage chronic conditions, capture payer incentives, and thr...Read more about Intergy
Popular Comparisons
Buyers Guide
Last Updated: March 16, 2023The prescription pad has been redesigned for the digital age, and it’s changing the way patients get the medication they need. Doctors are now turning to electronic prescribing (e-prescribing) software instead of paper-based notes to handle their prescription orders. In fact, according to Maryville University, just over 70% of physicians currently use e-prescribing software.
Software providers are taking notice of the demand for electronic prescription software. As a result, there are hundreds of solutions available for practices to purchase. In this guide, we’ll break down what you need to know before selecting the right e-prescribing software for your organization.
Here’s what we’ll discuss:
What Is E-Prescribing Software?
Common Functionality of E-Prescribing Software
What Is E-Prescribing Software?
E-prescribing software is a tool that allows you to electronically generate and transmit a prescription order directly from a healthcare provider to a patient’s pharmacy of choice. In other words, doctors can create and send a patient’s prescription using their computer or mobile device, rather than using manual methods (e.g., phone calls and faxes) to contact pharmacies.
Electronic prescriptions are transmitted through private, secure and closed networks maintained by e-prescribing software vendors. These networks are able to connect with the vast majority of pharmacies across the country.
The government has supported e-prescriptions by passing laws incentivizing their adoption, such as the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act (MIPPA) of 2003 and the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act of 2009. This is likely due to the software’s many benefits, which include:
Enhanced patient safety: Doctors and users can identify drug interactions and allergies before finalizing a prescription because of built-in alert systems integrated into the software.
Faster access to patient information: Prescribers can access a patient’s insurance formularies, eligibility information, and a list of current or past medications.
Improved accuracy: Doctors have access to patient histories at the click of a button which gives a more holistic picture of their health and reduces the chance of prescribing errors.
Increased patient convenience: Patients only need to take one trip to the pharmacist when filling or refilling a prescription because doctors can send medication orders digitally to the pharmacy.
Guaranteed legibility: Pharmacists won’t have trouble reading a prescriber’s handwriting with digitally sent prescriptions, making dosage and drug information more accurate.
Patient medication calendar (Source)
For all these reasons, electronic prescribing has been lauded as a more accurate, efficient and safe alternative to handwritten prescriptions.
Common Functionality of E-Prescribing Software
Software providers offer a variety of functional breadth and depth in their e-prescribing solutions. Here are some of the most common capabilities:
Medication selection | Prescribers can typically choose from more than one option when searching for a medication to include in the prescription order, including generic alternatives to brand-name drugs. |
Prescription creation and submission | Users can generate new prescriptions to be sent directly to a pharmacy from their desktop computer or mobile device. These orders can be processed individually or several at a time. Order management tools are typically included to ensure pharmacies have received prescriptions. |
Adverse interaction checks | Most systems offer alerts and warnings for a variety of potential adverse reactions from a particular prescription, such as drug interactions, allergies, dosage amounts and duplicates. |
Refill authorizations | Pharmacies can send refill requests to prescribers directly through the software's network. Providers can then approve or deny these requests electronically. |
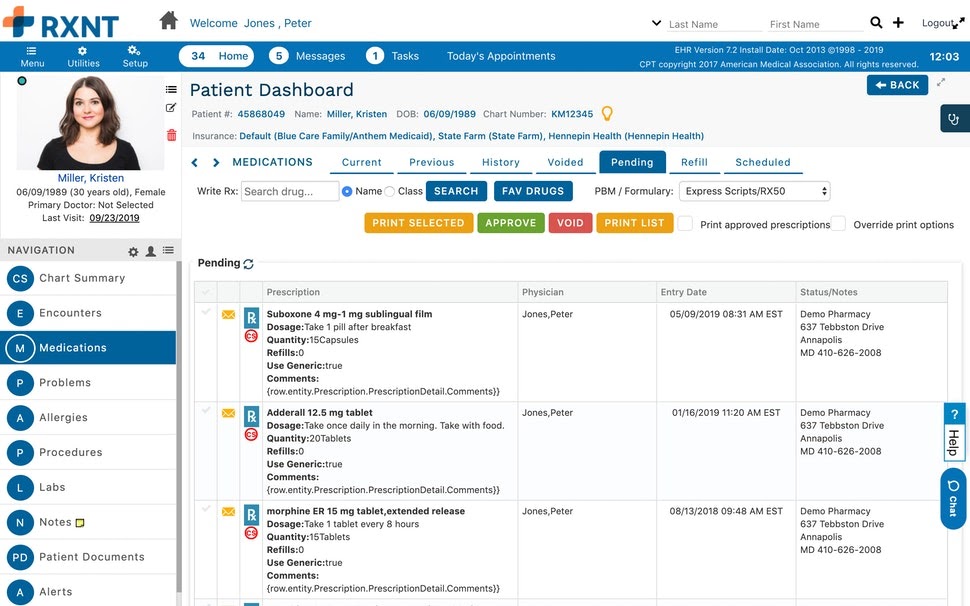
Medication history views | Most solutions allow users to access a patient’s medication history by importing it from a pharmacy’s database, or through the medication claims history provided by insurance payers/pharmacy benefit managers. |
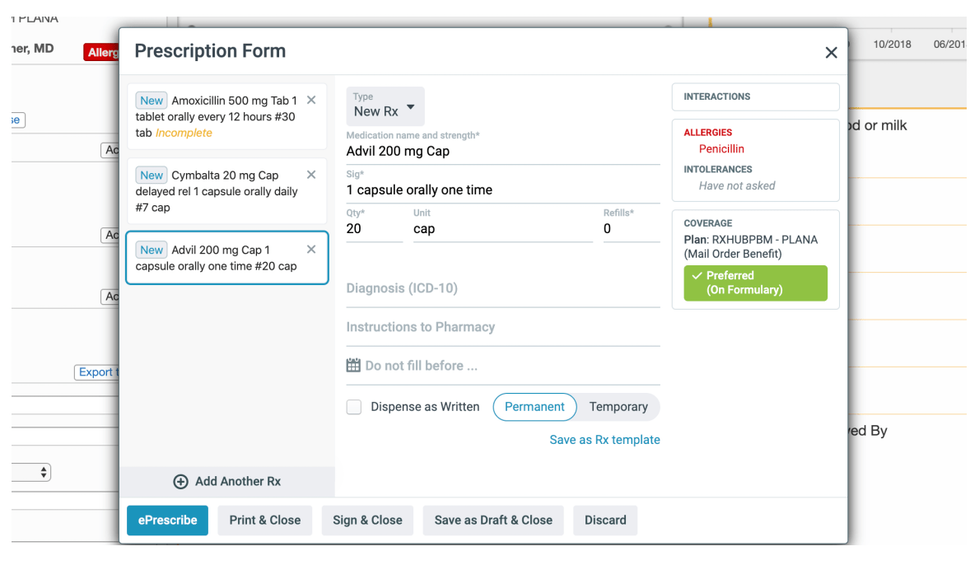
Doctor notes and allergy information when prescribing new medication (Source)
Deployment Strategies
E-prescribing vendors offer their products through one of two deployment models: standalone applications, or electronic health records (EHR) suites that include electronic prescription capabilities along with several other applications (e.g., patient scheduling and billing).
After all, it's easier to implement an e-prescribing system that’s integrated with a practice management solution out of the box. Integrating a third-party e-prescribing product with existing EHR software is generally more difficult.
On the other hand, standalone or “best-of-breed” programs have the benefit of being less expensive than EHR suites, in most cases. Since the user is only paying for one application as opposed to three or more, the fee for service isn’t usually as high.
Your budget and the size of your practice will be the determining factors when it comes to deciding between a best-of-breed system and an integrated EHR suite. Large and midsize practices with greater resources and multiple prescribers will likely be better served by comprehensive EHR suites than by standalone e-prescribing systems.
Market Trends to Understand
Government initiatives and incentive programs: One of the key drivers of adopting e-prescribing are the incentive programs launched by the government to improve healthcare quality, reduce healthcare costs and minimize prescription errors (Source: NCBI). The National Council for Prescription Drugs Program, a pharmacy standards development organization, has developed specialized standards for e-prescribing. The implementation of government initiatives, such as the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (2009), and Drug Enforcement Administration’s rule allowing electronic prescription of controlled substances (EPCS) have assisted in increasing the use of e-prescribing.
In Europe, eHealth projects, such as the Schleswig-Holstein Health initiative and European Patient Smart Open Services (epSOS), have helped increase the adoption of e-prescribing systems (Source: Persistence Market Research).
Investments in healthcare IT: Rising investments in healthcare IT have increased the adoption of EHR software and other technology. Gartner states that “digital healthcare is propelling spending in enhancing core automation systems like various health information systems and other associated technologies”. Improved infrastructure and expansion of healthcare IT have helped in the growth of e-prescribing technology. The growing adoption of integrated EHR models has also aided the e-prescribing market.
Advancements in e-prescribing technology: Persistence Market Research also says that advanced e-prescribing features, such as data security checks, patient history, preparing complete medication lists and information of formulary, are also key drivers of this market. These advancements have helped expand the scope and quality of patient care.
Improved efficiency and reduced expenses: According to Statista, 80% of all prescriptions are written digitally. This has helped the industry improve efficiency, reduce medication errors and enjoy cost-saving benefits.
High costs, security and connectivity issues hinder adoption of e-prescribing systems: The high costs of e-prescribing systems and risks associated with privacy and patient security restrain the growth of the e-prescribing market. Other factors include unavailability of high-speed broadband services and integrated networks, especially in developing countries. The absence of competent IT professionals and laws to protect patient privacy discourage pharmacies and healthcare professionals from switching to e-prescribing systems.
Conclusion
The shift to electronic prescribing systems can save funds and manual efforts in the healthcare industry. Additional features offered by these systems help to improve patient care efficiency. Improvements in IT infrastructure and investments in digital healthcare will help improve adoption of e-prescribing systems. Companies that become early adopters will reap the benefits sooner than those who don’t.







