Best Construction Categories
Best Facilities Management Categories
Best Human Resources Categories
Best Legal Management Categories
Best Manufacturing Categories
Best Medical Categories
Best Property Management Categories
Get 1-on-1 advice in 15 minutes. It's free.

Josh P.

A Guide to Billing and Invoicing Software Pricing Models
Billing and invoicing software automates the process of creating, sending, and tracking invoices for goods or services provided, allowing businesses to reduce their manual tasks and errors. However, with the given number of products available in the market, each with a different pricing model and functionality, navigating these options can be confusing.
With this in mind, we’ve created a guide to simplify billing software pricing for you. We provide clarity on the costs associated with top-rated billing and invoicing solutions, including price structures, subscription fees, implementation costs, and additional expenses. By offering a detailed pricing comparison, we aim to help you make an informed software purchase that fits your budget and billing and invoicing software needs.
What is billing and invoicing software?
Billing and invoicing software helps businesses generate and send professional invoices. These applications track multiple invoices, flag unpaid invoices, reduce manual data errors, and ensure timely collection of online payments. The core features of billing and invoicing software are invoice creation and invoice history.
What are the different types of billing and invoicing software pricing models?
Billing and invoicing software have different pricing plans or ranges determined by several factors, such as software features, the number of users, data storage capacity, business size, training availability, deployment options, and available integrations. Here are some common billing and invoicing software pricing models:
Subscription license
You pay a monthly or annual fee to use the software for a set period of time. Pricing is typically based on the number of users per month. The subscription model is commonly used for cloud-based deployments where the system is hosted by the software provider on their servers and can be accessed by your users on compatible devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets via the internet.
Some common types of subscription pricing options include:
Per user: Pricing is based on the number of users accessing the software. It can be either a flat fee per user or a tiered structure where the cost per user decreases as the number of users increases.
Tiered: Different pricing tiers based on the software features included, with higher tiers offering more advanced functionalities.
Per invoice: A fee is charged for each invoice created or processed.
Hybrid pricing: Combines multiple pricing models into a single plan. This can include elements of fixed monthly fees, per-invoice charges, usage-based pricing, or tiered pricing.
Flat rate: A single, fixed fee for a specified period, regardless of the number of users or invoices.
Pay as you go: Charges are based on the actual consumption of software resources, such as the number of invoices created, transactions processed, or storage space consumed.
Perpetual license
Under this pricing model, you pay a one-time upfront fee for the permanent license to own and use the billing and invoicing solution. The fee can vary based on the number of users. The perpetual pricing model is commonly used for on-premise deployments where the software is hosted and maintained in-house on your own servers.
Free and open source license
These pricing options are commonly used by small-business owners with limited budgets and resources.
Freemium: A basic version of the software is offered for free, with premium features, add-ons, or additional services available for a fee.
Open source: The software source code is freely available, allowing users to modify and distribute it. While the software is often free to use, you may incur implementation, maintenance, and customization costs.
Common subscription pricing tiers for billing and invoicing software
Under the subscription model, per-user pricing is the most commonly seen. You pay a fixed fee for every user seat, and prices increase as the number of user seats increases. Per-user pricing plans are typically of three types, according to analysis by our research team.
Entry-level plans (one to four users): These plans cost up to $32 per month and offer access to standard billing software features. They are suitable for small businesses with basic billing and software needs, such as invoice creation, templates, and payment processing.
Mid-tier plans (five to nine users): The costs go up to $141 per month and offer advanced features, such as automated workflows, role-based access, recurring payments, payment reminders, customer relationship management, and advanced analytics. These plans are suitable for businesses that have outgrown entry-level billing and invoicing tools but don’t require the full range of functionality offered by enterprise-level systems.
High-end plans (10+ users): Costing up to $259 per month, the high-end plans offer unlimited features from entry-level and mid-tier plans and a range of advanced billing and invoicing capabilities, including sales pipeline management, revenue cycle management, priority customer support, and advanced payment options, such as electronic bank transfers and integration with a wide range of payment gateways. These plans suit larger enterprises with complex billing and invoicing needs, including high-volume transactions, comprehensive analytics, and customization requirements.
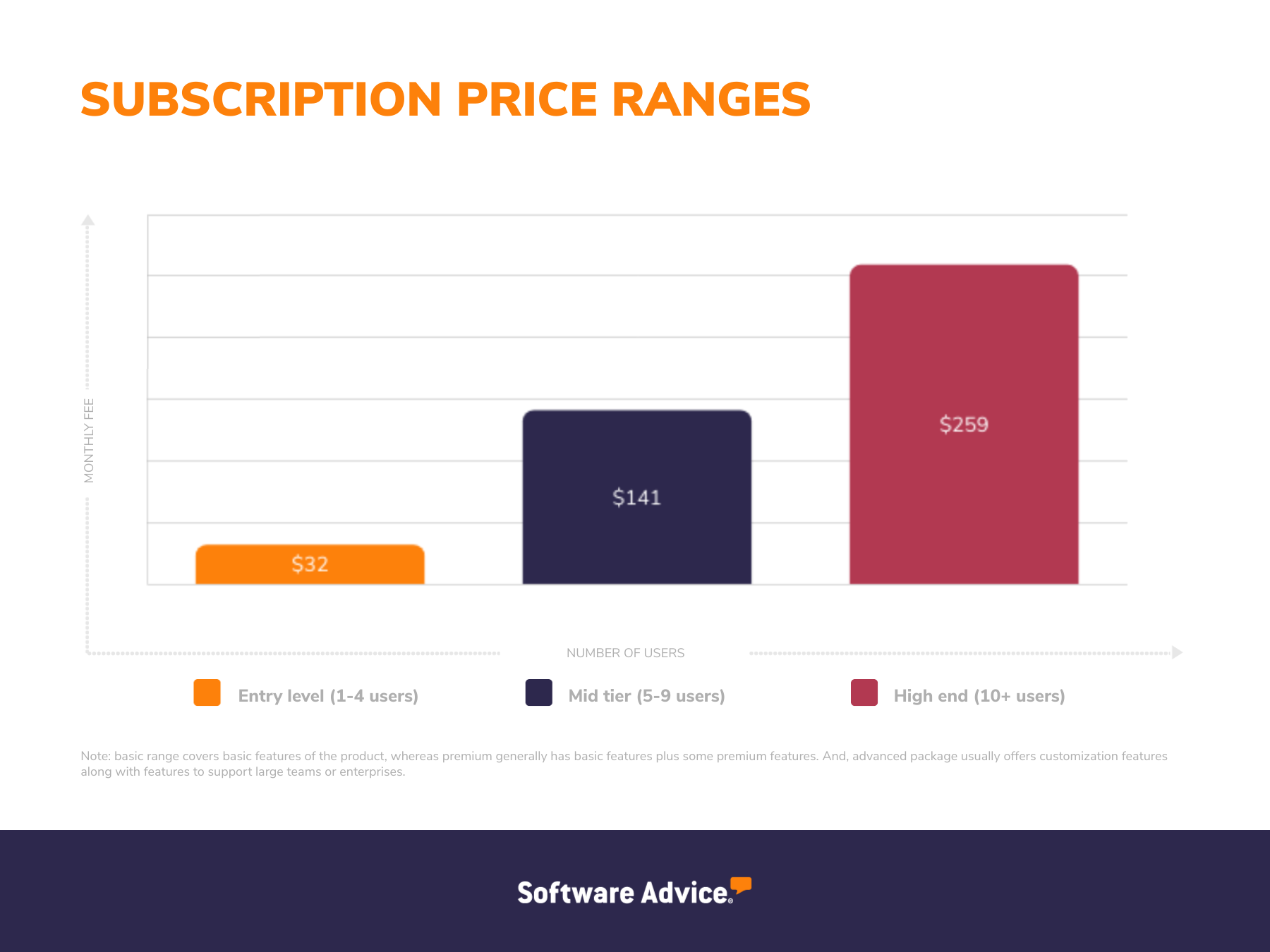
For reference, below is a snapshot of the prices of the most reviewed billing and invoicing solutions with subscription pricing plans. These products are taken from the most recent Software Advice FrontRunners report for billing and invoicing software.*
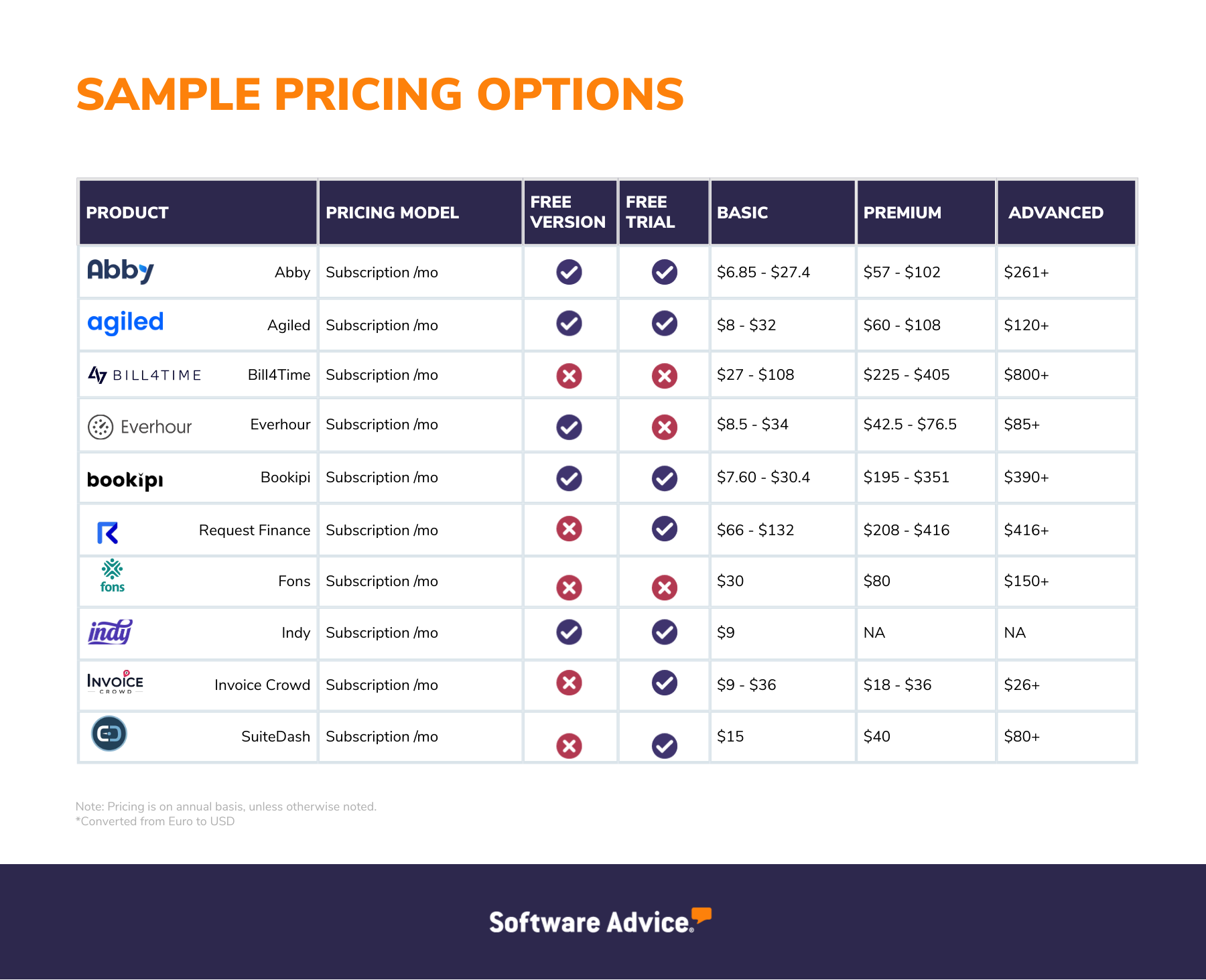
Note: To find out the subscription price of each tier (entry level, mid tier, and high end), we calculated the median value based on their respective pricing mentioned in the product pricing table above. In this case, the median represents the middle value of the monthly fee for each pricing tier when all the top-rated software solutions are considered. While average pricing may be easily skewed by outliers, the median value gives users an understanding of the midpoint of ranges they're likely to encounter.
What are the upfront and recurring costs associated with billing and invoicing software?
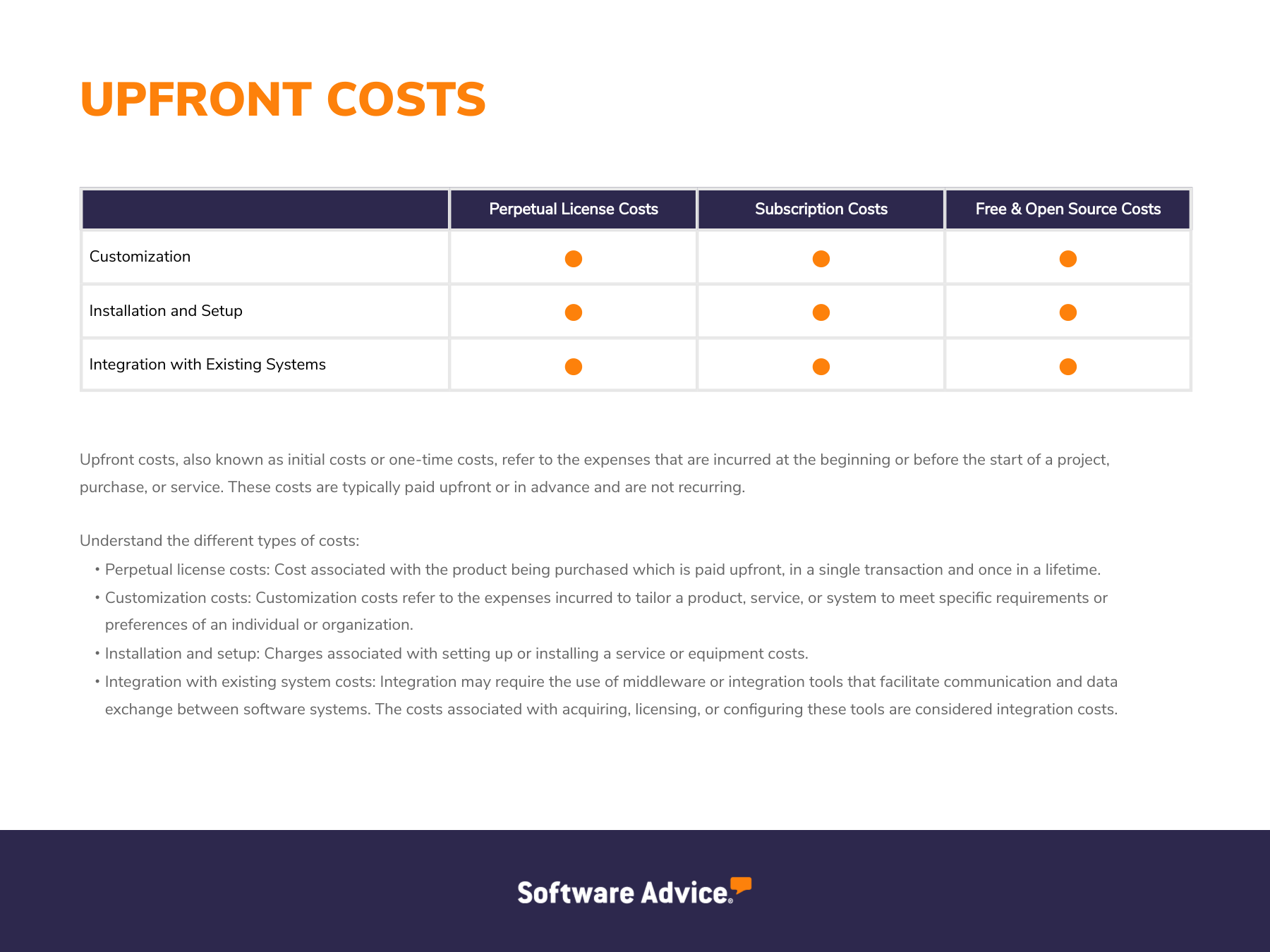
Upfront costs are the initial expenses incurred when purchasing or subscribing to software, such as licensing, installation, setup, and training. The graphic below illustrates the primary upfront costs associated with billing and invoicing software.
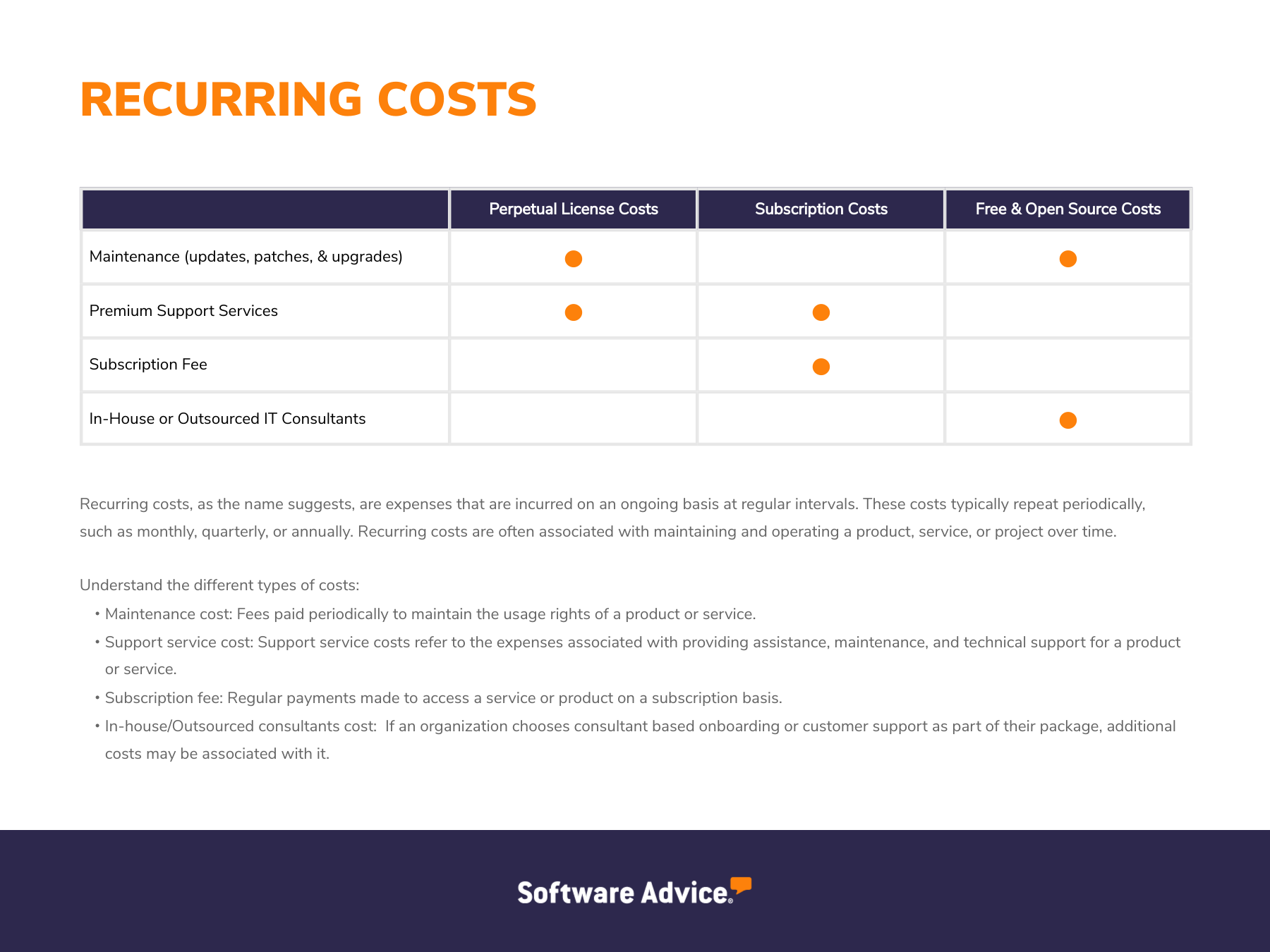
Recurring costs are the ongoing expenses associated with using software, such as subscription fees and maintenance costs. These costs may be charged monthly or annually and can also include expenses for upgrades or additional user licenses. The graphic below shows the primary recurring costs associated with billing and invoicing software.
| Subscription license | Perpetual license | Free and open source license |
|---|---|---|---|
Upfront costs | Installation, setup, and software customization. | One-time license fee, hardware (e.g., servers, storage devices, network infrastructure equipment), and installation charges. | Open source plans may involve installation and setup expenses—free plans don’t have any upfront costs. |
Recurring costs | Monthly or annual subscription fee and premium customer support offerings (e.g., 24/7 phone support hours, quick ticket response time). | Monthly, annual, or ad hoc maintenance (e.g., updates, patches, upgrades) and premium support offerings (e.g., extended phone support hours). | Free plans don’t have recurring costs; open source plans can include fees for server hosting, additional features, and IT staff hours to modify the source code. |
Hidden costs | Customization, implementation of unique company branding, and integration with existing software, such as accounting, customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and time tracking systems. | Customization, integration, and costs for hiring IT staff for maintaining servers. | Implementation, customization, maintenance, integration with existing tech stack, training, and premium support costs could apply to both free and open source plans. |
What are the additional costs associated with billing and invoicing software?
These additional costs are common across different software providers and pricing models, so it’s important to include them in your budget.

Data migration: These costs involve transferring business-critical data, such as customer information, invoice history, and payment records, from previous systems or spreadsheets to the new billing and invoicing software. Data migration costs can vary depending on the volume and complexity of the data.
Training: Staff members need to be adequately trained to maximize the benefits of the new billing and invoicing software. Training includes learning to use the software features, understanding new workflows, and adapting to billing process changes. These costs can vary depending on the complexity of the software, the size of your team, and the chosen training method.
Hardware and IT: These costs include the cost of servers required to host the software and database, additional physical storage for backing up large transactional data, routers and network cable costs to ensure reliable connections, and employee computers to access the software. Additionally, these may include the cost of hiring IT staff to manage and maintain the new system.
Maintenance and upgrades: Maintenance and upgrade costs often vary based on the deployment types (on-premise vs. cloud-based). In general, these costs cover the charges associated with software updates to fix bugs, feature enhancement, server repairs, security patch installation, firewall updates, and troubleshooting. Maintenance and upgrades are necessary to ensure that the software functions optimally and incorporates the latest features and security patches.
How to find the right pricing plan for billing and invoicing software
Evaluate your billing and invoicing needs: Before investing in the best billing software, consider how many people are likely to use the software or require access to the tool. Additionally, identify the features that you require. These may include expense tracking, invoice templates, recurring billing, payment reminders, or integration with existing systems, such as legal billing, expense tracking, payment processing, and accounting software. Plans with advanced billing and invoicing features and functionalities, such as advanced reporting, subscription management, white labeling, offline access, and AI-powered automation capabilities generally have a higher price tag than the basic options.
Determine the number of users: The number of users who will need access to your billing and invoicing software is a crucial factor in determining the appropriate pricing plan. A basic plan might be sufficient for limited users, but a high-end plan would be more appropriate if you have a large number of users or more complex workflows. Software providers often base their pricing on the number of users. Knowing the exact number allows you to select a pricing plan that aligns with your budget and requirements.
Evaluate different vendors: Evaluating multiple vendors is another important step in finding the right pricing plan for your billing and invoicing software.You can identify potential vendors through online searches, industry recommendations, and networking. Once you have shortlisted a few vendors, analyze the pricing structures offered by each one of them and the features included in each pricing plan. By comparing offerings from different providers, you can identify the best value for your money and ensure that the software meets your specific needs.
Common questions to ask when choosing billing and invoicing software
When evaluating the pricing plans of the best billing software, it is essential to ask the right questions to ensure you are making an informed decision. Here are some important questions to consider:
Is there a free trial or demo version of the software?
A free trial or demo version of the tool helps you understand the software's features, user interface, and overall suitability for your business. This hands-on experience is a good way to ensure that the software aligns with your billing and invoicing needs, fits your current workflows, and integrates with your existing systems.
Are there any additional costs associated with the tool?
Additional fees or hidden costs associated with billing and invoicing software can significantly impact your overall expenses. These costs may include data migration fees, training fees, integration charges, support fees, and costs associated with additional storage space. Understanding these costs can help you make an informed decision and avoid unexpected expenses.
Is there any volume discount?
Volume discounts are a common pricing strategy used by billing and invoicing software providers to incentivize larger businesses or those with high usage levels. These discounts typically involve offering a reduced rate per user, per invoice, or per transaction when the volume of business exceeds a certain threshold. By understanding these and negotiating effectively, you can potentially save money on your software purchase.
What are the best billing and invoicing software packages?
Do the billing and invoicing software tools listed in this guide fall within your budget? If yes, compare their features and read real user reviews of more than 1,000 similar products listed on our billing and invoicing category page.
Methodology
*The products featured in this guide qualified for the most recent billing and invoicing software FrontRunners report and were highly rated by users.
Only products with publicly available pricing information were included in this table. We summarized publicly available pricing sources, including vendor websites as of September 2024, beginning with the lowest monthly pricing (not including annual discounts) for packages that include the core functionality for this software category.
The core features of these billing and invoicing software tools include invoice creation and invoice history.
We have also listed pricing for more advanced packages (per user, when available) that include these core software feature(s). As always, your company’s specific needs may differ, and final pricing will vary.
Note: This article is intended to inform our readers about business-related concerns in the U.S. It is in no way intended to provide financial advice or to endorse a specific course of action. For advice on your specific situation, consult your accountant or financial consultant.