Best EAM software of 2026: which is right for you?

- Popular Comparisons
- FrontRunners
- Buyers Guide
Compare Products
Showing 1 - 25 of 161 products
Compare Products
Sort by
Reviews: Sorts listings by the number of user reviews we have published, greatest to least.
Average Rating: Sorts listings by overall star rating based on user reviews, highest to lowest.
Alphabetically (A-Z): Sorts listings by product name from A to Z.

MaintainX is a maintenance and asset management platform built for industrial and frontline teams. It helps organizations stream...Read more about MaintainX
MaintainX's Best Rated Features
See All
MaintainX's Worst Rated Features
See All

Fiix is a cloud-based computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) that helps businesses organize their maintenance departm...Read more about Fiix
Fiix's Best Rated Features
See All
Fiix's Worst Rated Features
See All

Maint CMMS is a cloud-based solution that enables maintenance professionals to monitor, capture, store and share historical asse...Read more about eMaint CMMS
eMaint CMMS's Best Rated Features
See All
eMaint CMMS's Worst Rated Features
See All

Manage your fixed assets from acquisition to disposal with our best-in-class, comprehensive solution, Sage Fixed Assets. Capture...Read more about Sage Fixed Assets
Sage Fixed Assets's Best Rated Features
See All
Sage Fixed Assets's Worst Rated Features
See All

Maintenance Connection is a multi-site, multi-industry CMMS and EAM tool that streamlines maintenance operations across industri...Read more about Maintenance Connection
Maintenance Connection's Best Rated Features
See All
Maintenance Connection's Worst Rated Features
See All

Limble is a CMMS platform designed to optimize maintenance operations and improve compliance. Its work order management allows u...Read more about Limble
Limble's Best Rated Features
See All
Limble's Worst Rated Features
See All

EZO is a cloud-based asset management software designed to help organizations track, manage, and maintain physical assets from a...Read more about EZO
EZO's Best Rated Features
See All
EZO's Worst Rated Features
See All

IFS Cloud is a composable enterprise software application that orchestrates customers, people, and assets to reduce complexity, ...Read more about IFS Cloud

eWorkOrders CMMS is a cloud-based computerized maintenance management system designed to streamline maintenance operations and e...Read more about eWorkOrders CMMS
eWorkOrders CMMS's Best Rated Features
See All
eWorkOrders CMMS's Worst Rated Features
See All

CHAMPS CMMS is a cloud-based computerized maintenance management system and enterprise asset management (EAM) solution designed ...Read more about CHAMPS CMMS

MaintiMizer is a comprehensive suite of enterprise asset management (EAM) solutions and computerized maintenance management syst...Read more about MaintiMizer

Proactively manage your assets, simplify work orders, plan capital improvement projects, and make the most of your resources wit...Read more about OpenGov Enterprise Asset Management

WebTMA is a reliable, flexible maintenance management solution trusted by over 1,000 organizations, managing over 55,000 facilit...Read more about WebTMA
WebTMA's Best Rated Features
See All
WebTMA's Worst Rated Features
See All

Sigga EAM Power is designed for plant maintenance teams for a step-change improvement in KPIs. The application is provided on a ...Read more about Sigga EAM Empower
No reviews yet
recommendations

Looking for an easier way to keep track of your equipment, software, and inventory? Hector is a cloud-based asset inventory mana...Read more about Hector

iM3 SCM’s Smart Warehouse Management (smartWMS) is a cloud-based software offered to its customers as a SaaS Application. iM3 SC...Read more about iM3 SCM Suite
iM3 SCM Suite's Best Rated Features
See All
iM3 SCM Suite's Worst Rated Features
See All

UpKeep is a web-based CMMS offering a mobile-first solution for maintenance teams, streamlining operations with asset and workfl...Read more about UpKeep
UpKeep's Best Rated Features
See All
UpKeep's Worst Rated Features
See All

Facilio provides a Connected CMMS platform that helps you to unify all your property operations and maintenance to get real-time...Read more about Facilio
Facilio's Best Rated Features
See All
Facilio's Worst Rated Features
See All

Timly is a cloud-based inventory management solution designed for small and large businesses. The tool digitizes inventory proce...Read more about Timly
Timly's Best Rated Features
See All
Timly's Worst Rated Features
See All

Fracttal One is a smart maintenance platform designed to help organizations manage their maintenance operations using AI-powered...Read more about Fracttal One
Fracttal One's Best Rated Features
See All
Fracttal One's Worst Rated Features
See All

Infraspeak is a collaborative platform that enables end-to-end collaboration, visibility and efficiency to facilities management...Read more about Infraspeak
Infraspeak's Best Rated Features
See All
Infraspeak's Worst Rated Features
See All

Asset Panda is a cloud-based platform for facility managers that offers a suite of applications including asset tracking and mai...Read more about Asset Panda
Asset Panda's Best Rated Features
See All
Asset Panda's Worst Rated Features
See All

TRACTIAN is an AI-enabled condition monitoring and asset performance management solution that enhances industrial operations. It...Read more about TRACTIAN
TRACTIAN's Best Rated Features
See All
TRACTIAN's Worst Rated Features
See All

SafetyCulture is a mobile-first inspection platform that allows teams to digitize their operations. As an inspection management ...Read more about SafetyCulture
SafetyCulture's Best Rated Features
See All
SafetyCulture's Worst Rated Features
See All

AssetTiger is a cloud-based asset management software designed to help businesses streamline processes related to maintenance sc...Read more about AssetTiger
AssetTiger's Best Rated Features
See All
AssetTiger's Worst Rated Features
See All
Popular Comparisons
Your Guide to Top EAM Software, November 2022
Software Advice uses reviews from real software users to highlight the top-rated EAM products in North America.
Learn how products are chosenExplore FrontRunners
“Usability” includes user ratings for Functionality and Ease of Use.
“Customer Satisfaction” includes user ratings for Customer Support, Likelihood to Recommend and Value for Money.
Reviews analysis period: The reviews analysis period spans two years and ends the 15th of the month prior to publication.
Buyers Guide
This detailed guide will help you find and buy the right enterprise asset management software for you and your business.
Last Updated on January 27, 2025Enterprise asset management (EAM) software offers businesses a way to manage maintenance, spare parts inventory and asset tracking across an enterprise. In terms of functionality, EAMs are related to traditional computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS)—but EAM software goes further, helping manage the entire life cycle of equipment and other assets.
In this guide, we’ll describe the common capabilities of EAMs, the benefits they provide and a comparison between EAM and CMMS software. This can help buyers determine the right system for their needs. We’ll cover:
Common Functionality of EAM Software
What Is EAM Software?
An EAM system is sometimes described as a “CMMS on steroids,” but this is a bit of an oversimplification. As a starting point, however, let’s review the common functionality of a CMMS:
Preventive and predictive maintenance
These tools help users manage the maintenance of assets and equipment, from generating work orders to using reports to identify areas of improvement. Many EAM systems will offer CMMS functionality. But an EAM takes it to the next level, adding complete life cycle management functionality to help users realize the full return on investment in assets.
EAM systems emerged in the 1990s, as tools to take advantage of computer networking via the Internet. Instead of using isolated CMMSs at each facility, companies could adopt just one EAM system and standardize with it across the enterprise.
Today, several CMMS vendors have morphed their product into an EAM system, added features or marketed their system as handling both. So, while the distinction is blurry, the rise of EAM gives larger companies robust tools for their enterprise maintenance goals.
In short, companies will want to use an EAM when taking a more holistic, analytical view of operations. A CMMS is a repository for data—but an EAM system can facilitate data-driven decision-making.
The chart below shows some basic differences between CMMS and EAM functionality:
CMMS | EAM |
Track and store machinery and spare parts | Track and store machinery and spare parts as well as broader asset categories, including IT assets and facilities |
Analyze data about machine downtime, work order completion rates and maintenance costs | Analyze data about all types of assets and financial information for departments and locations at a high-level |
Schedule and track maintenance through work orders | Schedule and track maintenance; plan and follow capital projects through completion |
Common Functionality of EAM Software
EAM applications expand the scope of a stand-alone CMMS beyond maintenance management, in order to maximize the useful life of assets. These applications can include:
Asset hierarchy. Forming an asset hierarchy helps keep track of several pieces of equipment across multiple locations. For example, a company may want to group CNC (computer numerical control) machines separate from manually controlled machines, both under the umbrella of “plant machines.” Going further, each CNC machine can be separated into its individual components, giving management a full view of all assets, their component parts and how they are related. In addition, users can assign owners to assets, which helps keep things organized when scheduling work.
Purchasing and procurement management. These tools can help with ordering spare parts, requesting quotes and logging other vendor information. Many systems will remind users to order parts based on established minimums or dates, and can store information about vendors, such as average delivery times and pricing. With this information logged, management can more efficiently manage inventory by generating reports and analyzing data.
Project management. This allows users to generate projects and organize budgets, assets and employees from start to finish. Project management tools can display various metrics and key performance indicators, such as expected finish dates and planned versus actual costs. For example, EAM users may want to track the progress of an equipment overhaul in a particular department, or monitor the construction of a new facility.
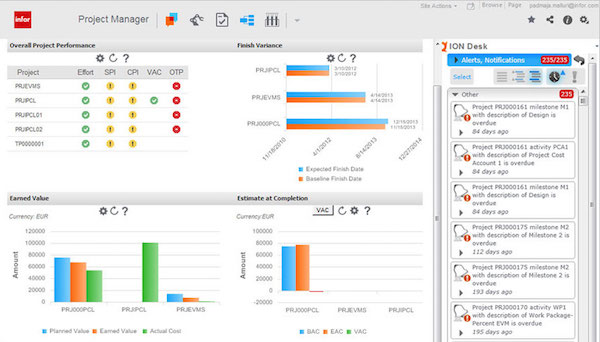
Project management metrics as shown in Infor EAM
Condition monitoring. This application can be found in both a CMMS and an EAM. It offers maintenance personnel a way to monitor an asset’s operating conditions by streaming real-time data, collected via sensors, into the system. This allows for the most accurate readings, so problems are identified as early as possible.
Safety management. This helps management stay on top of all policies related to fostering a safe workplace environment. In it, users can store related documents, define procedures and establish responsibilities for employees in case of workplace hazards.
Inspection management. Manage occasional inspections on equipment, and automatically generate work orders when inspection results fall outside established ranges.
What Type of Buyer Are You?
Before evaluating systems, determine which type of buyer you are:
Small-business maintenance manager. At many companies, a maintenance manager is primarily focused on completing work orders in an appropriate time frame, reducing labor and inventory costs and maximizing the availability of critical equipment. A traditional CMMS can meet these needs, and the extra functionality found in many EAMs—including project management or inspection management—may go unused.
Maintenance manager with multiple locations or facilities. Midsize to large companies are more likely to realize the full value of an EAM’s wide range of functionality. Managers who will be tracking and maintaining assets across an enterprise, with multiple locations and departments, can use an EAM to dissect data and make informed decisions and projections. And, of course, you’ll still get all the benefits of core CMMS features.


